Abstract
The choice between Basiliximab (BSX) or Anti-Thymocyte Globulin (ATG) as induction therapy in non-immunized kidney transplant recipients remains uncertain. Whilst ATG may allow steroid withdrawal and a decrease in tacrolimus, it also increases infectious complications. We investigated outcomes in non-immunized patients receiving a very low dosage of ATG versus BSX as induction. Study outcomes were patient/graft survival, cumulative probabilities of biopsy proven acute rejection (BPAR), infectious episode including CMV and post-transplant diabetes (PTD). Cox, logistic or linear statistical models were used depending on the studied outcome and models were weighted on propensity scores. 100 patients received ATG (mean total dose of 2.0 mg/kg) and 83 received BSX. Maintenance therapy was comparable. Patient and graft survival did not differ between groups, nor did infectious complications. There was a trend for a higher occurrence of a first BPAR in the BSX group (HR at 1.92; 95%CI: [0.77; 4.78]; p = 0.15) with a significantly higher BPAR episodes (17% vs 7.3%, p = 0.01). PTD occurrence was significantly higher in the BSX group (HR at 2.44; 95%CI: [1.09; 5.46]; p = 0.03). Induction with a very low dose of ATG in non-immunized recipients was safe and associated with a lower rate of BPAR and PTD without increasing infectious complications.

Introduction
The choice for induction therapy in patients with low immunological risk remains uncertain. Basiliximab (Simulect®) is a monoclonal antibody targeting the IL-2 receptor. It results in decreased T cell activation without inducing T cell depletion which has proven beneficial versus placebo controls in induction therapy of kidney transplant recipients (1). Anti-thymocyte Globulins (ATG) consists of polyclonal globulins exerting a strong T cell depleting effect which has proven beneficial against the occurrence of biopsy proven acute rejection (BPAR) in high immunological risk recipients compared to Basiliximab (2). However, this T cell depletion has also been associated with an increased risk of infectious complications, and notably, CMV reactivation (3). Thus, the kidney disease improving global outcomes (KDIGO) guidelines recommends Basiliximab as first line induction therapy in patients with low immunological risk in association with a triple maintenance therapy consisting of calcineurin inhibitors (CNI)—mainly tacrolimus –, antiproliferative drugs (mycophenolate mofetil—MMF; or mycophenolic acid—MPA) and steroids (4). However, ATG remains widely used due to its good protective effect against allograft rejection and other benefits such as a decrease in delayed graft function (5) or the possibility of rapid steroid withdrawal, thus permitting reduction in side effects such as post-transplant diabetes (6, 7). Moreover, ATG’s depleting effect has been proven to depend on the total administered dose, which is currently lower than when first introduced several years ago (8).
In our institution, induction therapy is mainly standardized, even though transplant physicians are free to modify treatment according to the patients’ history. Briefly, induction of non-immunized patients receiving a first kidney transplant consisted mostly of Basiliximab until 2016; and of a very low dose of ATG since 2017. The objective of this study was to retrospectively evaluate the impact of this induction modification on post-transplant outcomes, notably, immunological complications (BPAR and occurrence of de novo donor specific antibodies—dnDSA), infectious complications and side effects such as occurrence of post-transplant diabetes (PTD).
Materials and Methods
Studied Population
The included patients were adults ≥18 years receiving a first kidney transplantation from heart beating deceased donors, treated with either ATG or Basiliximab (BSX) as induction therapy between 2015 and 2020. Multiple organ transplant recipients were not considered. We only included patients without anti-HLA class I and/or class II antibodies as determined by Luminex® assay (i.e., mean fluorescence index <2000) and without pretransplant DSA determined at a MFI threshold of 1000 at the time of transplantation. The patients in the BSX group received 20 mg of Simulect® (Novartis) intravenously at day 0 and day 4. The patients in the ATG group received 75 mg of thymoglobulin (Sanofi) for 2 days (day 0 and day 1); however, if they weighed 50 kg or less they received only 50 mg of thymoglobulin. All patients received initial corticotherapy during the first days following transplantation (one 500 mg pulse in the BSX group, two 250 mg pulses in the ATG group, followed by oral steroid therapy which was rapidly reduced and withdrawn according to physician’s choice) associated with a maintenance immunosuppressive therapy consisting mainly of tacrolimus with antiproliferative drugs (mycophenolate mofetil or mycophenolic acid). Infectious prophylaxis consisted of trimethoprim + sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim®) during at least the first 6 months post transplantation, and until CD4+ T cells counts were ≥200/mm3, associated with valganciclovir depending on the risk of post-transplant CMV viremia (3 months in case of recipient’s positive serological assay; 6 months in case of recipient’s negative serological assay associated with a transplant from a CMV seropositive donor).
Available Data
Donor features included allograft status (extended criteria donor or standard criteria donor), donor age, donor sera creatininemia, cause of death, and CMV status. Recipient characteristics included age, gender, BMI, comorbidities (diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidaemia, neoplasia, vascular, cardiovascular history), duration on waiting list, pre-emptive transplantation, and CMV serology status. Transplantation parameters were the cold ischemia time (CIT), use of machine perfusion and the number of HLA-A-B-DR incompatibilities. Patients lost during follow-up were right-censored for mid- or long-term time-to-event. We assumed that the corresponding information were non-informative. For missing data, we voluntarily excluded patients for which the value spread from the initial date was too high (>3 months for 1-year analysis).
Outcomes
The principal outcome was patient and graft survival, defined by the time between the transplant and the first event requiring return to dialysis, pre-emptive re-transplantation, or death with a functioning graft. Secondly, we studied cumulative probabilities of all infectious complications (bacterial, BkV viremia or BkV nephropathy, CMV viremia or fungal infection), CMV viremia only, occurrence of the first biopsy proven acute rejection episode [BPAR according to the Banff classification (9)], occurrence of post-transplant malignancy and occurrence of post-transplant diabetes (PTD) (for this latter analysis, patients with diabetes before transplantation were excluded).
Protocol biopsies were performed at 3- and 12-month post transplantation. According to KDIGO recommendations, we considered indicated biopsies for suspicion of rejection by the occurrence of one criterion amongst the following: increased creatininemia (>25%) without any explanation, delayed graft function >10 days, occurrence of de novo donor specific anti-HLA antibody, new onset of proteinuria, or unexplained proteinuria >3 g per day. Occurrence of de novo DSA detected by Luminex® assay, and the eGFR (estimated by MDRD) at 1-year post transplantation were also evaluated (patients that died or were lost during follow-up before the first anniversary were excluded).
Statistical Analysis
The characteristics at the time of transplantation between ATG and BSX groups were compared using Chi-square tests or Fisher’s exact test for categorical variables and using Student t-tests for continuous variables. To consider possible confounding variables, we weighted the models on the propensity scores (10), which were obtained by a multivariable logistic regression. To consider possible confounders, we weighted the contribution of individuals according to inverse probability (inverse probability weighting - IPW) of the propensity score (PS) (11). The PS was estimated by a multivariable logistic regression with splines on continuous covariates to ensure the log-linearity assumption. If the splines had an OR greater than 10 or less than 0.1 in univariate analysis, the variable was categorized. Stabilized weights were used in order to obtain a pseudo dataset with a similar sample size to the original one and to estimate the average treatment effect in the entire population (ATE) of the exposure (12). The goodness-of-fit of the model was assessed by graphically checking the positivity assumption (Supplementary Figure S1) and studying the standardized differences (Supplementary Tables S1–S7). The adjusted survival curves were obtained using the weighted Kaplan-Meier estimator and compared using the adjusted log-rank test (13). To provide a relative measure of the effect, a Cox model was estimated maximizing the partial weighted likelihood and using a robust estimator for the variance (14). The corresponding hazard proportionality was graphically checked by plotting log-minus-log of the survival function for the variable of interest. Statistical analyses were performed using Plug-Stat® software (www.labcom-risca.com/plug-stat) based on the R software (15). Note, to respect the methodology in causal inference, we did not consider the maintenance therapy in the propensity scores as physicians may adapt the treatment according to the initial induction therapy.
Ethics Statement
Data were extracted from the French DIVAT cohort (www.divat.fr, approved by the CNIL, n°914184) consisting of recipients monitored in Nantes. The quality of the DIVAT data bank is validated by an annual cross-center audit. All participants gave informed consent. All patients were included and extracted from the DIVAT database, after informed consent. In order to respect confidential medical information, all data were anonymized before analysis.
Results
Description of the Cohort
The study flow-chart is presented in Figure 1. The characteristics of the 183 studied patients at the time of transplantation are presented in Table 1. 83 patients were in the BSX group (45.4%) versus 100 in the ATG group (54.6%). The average total dose of thymoglobulin administered was 2.0 mg/kg, and no serious side effects were noted in this population (notably no serum sickness disease). Of note, 49 patients in the ATG group received ≤2.0 mg/kg of thymoglobulin, while the average dosage of the 51 other patients was 2.3 mg/kg of thymoglobulin.
FIGURE 1
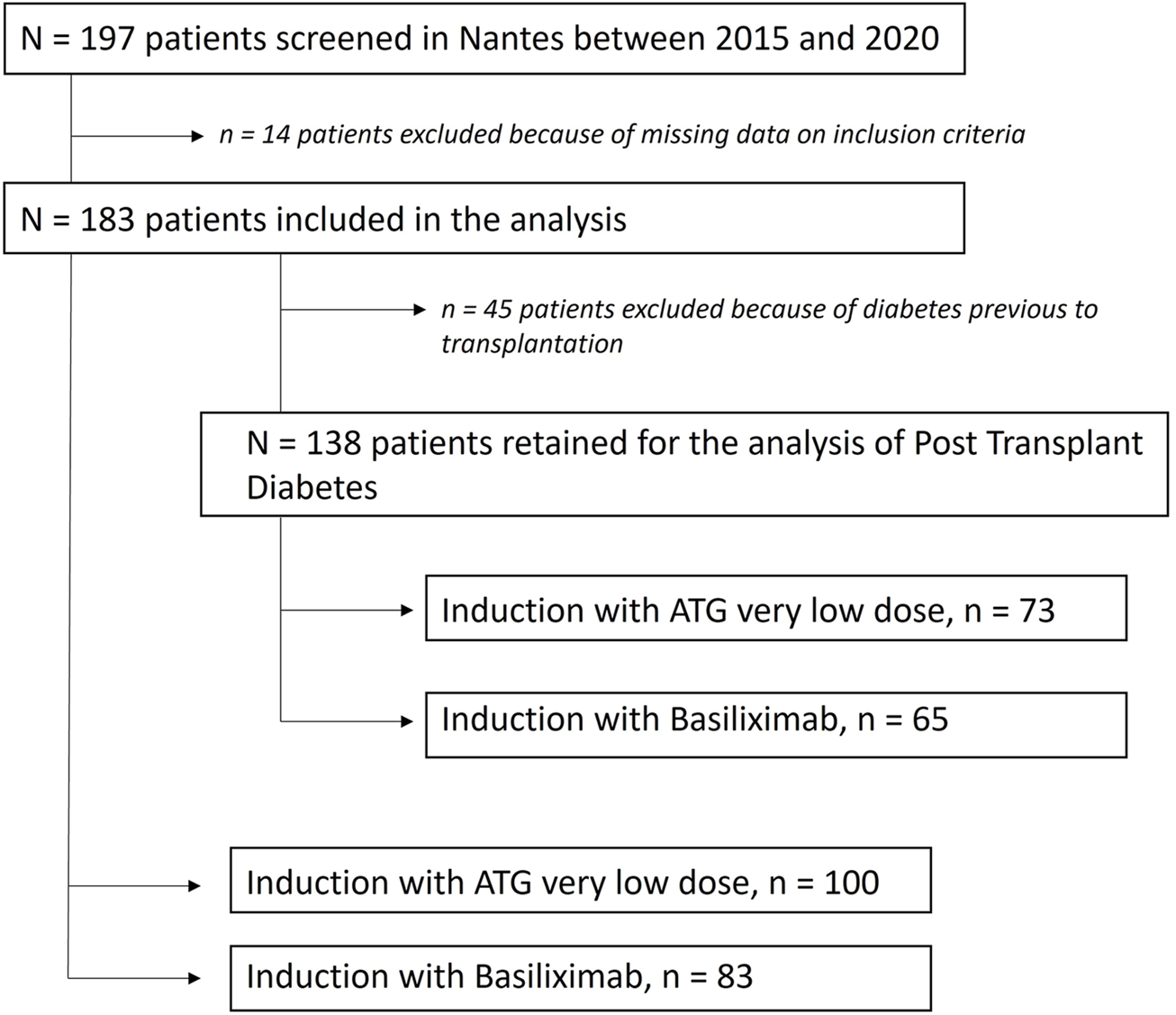
Flow chart of the study.
TABLE 1
| Whole sample (n = 183) | ATG (n = 100) | Basiliximab (n = 83) | p-value | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NA | n | % | NA | n | % | NA | n | % | ||
| Male recipient | 0 | 131 | 71.6 | 0 | 76 | 76.0 | 0 | 55 | 66.3 | 0.1460 |
| Preemptive transplantation | 0 | 33 | 18.0 | 0 | 15 | 15.0 | 0 | 18 | 21.7 | 0.2415 |
| Etiology of ESRD | ||||||||||
| Glomerulonephritis | 0 | 53 | 29.0 | 0 | 28 | 28.0 | 0 | 25 | 30.1 | 0.7529 |
| Tubulo-interstitial (including PKD) | 0 | 60 | 32.8 | 0 | 32 | 32.0 | 0 | 28 | 33.7 | 0.8034 |
| Vascular (including Hypertension) | 0 | 34 | 18.6 | 0 | 21 | 21.0 | 0 | 13 | 15.7 | 0.3554 |
| Diabetes | 0 | 19 | 10.4 | 0 | 11 | 11.0 | 0 | 8 | 9.7 | 0.7637 |
| Undetermined | 0 | 17 | 9.2 | 0 | 8 | 8.0 | 0 | 9 | 10.8 | 0.5095 |
| History of diabetes | 0 | 45 | 24.6 | 0 | 27 | 27.0 | 0 | 18 | 21.7 | 0.4060 |
| History of vascular disease | 0 | 72 | 39.3 | 0 | 41 | 41.0 | 0 | 31 | 37.3 | 0.6148 |
| History of cardiac disease | 0 | 65 | 35.5 | 0 | 43 | 43.0 | 0 | 22 | 26.5 | 0.0203 |
| History of cardiovascular disease | 0 | 100 | 54.6 | 0 | 60 | 60.0 | 0 | 40 | 48.2 | 0.1102 |
| History of pregnancy | 0 | 37 | 20.2 | 0 | 17 | 17.0 | 0 | 20 | 24.1 | 0.2341 |
| History of malignancy | 0 | 45 | 24.6 | 0 | 24 | 24.0 | 0 | 21 | 25.3 | 0.8387 |
| History of dyslipidemia | 0 | 114 | 62.3 | 0 | 60 | 60.0 | 0 | 54 | 65.1 | 0.4820 |
| Recipient BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 | 0 | 92 | 50.3 | 0 | 52 | 52.0 | 0 | 40 | 48.2 | 0.6081 |
| Positive recipient CMV serology | 1 | 75 | 41.2 | 1 | 45 | 45.5 | 0 | 30 | 36.1 | 0.2038 |
| HLA incompatibilities > 4 | 0 | 52 | 28.4 | 0 | 32 | 32.0 | 0 | 20 | 24.1 | 0.2379 |
| Use of machine perfusion | 0 | 111 | 60.6 | 0 | 62 | 62.0 | 0 | 49 | 59.0 | 0.6516 |
| Male donor | 0 | 108 | 59.0 | 0 | 56 | 56.0 | 0 | 52 | 62.7 | 0.3624 |
| ECD donor | 0 | 112 | 61.2 | 0 | 60 | 60.0 | 0 | 52 | 62.7 | 0.7141 |
| Vascular cause of death | 0 | 115 | 62.8 | 0 | 63 | 63.0 | 0 | 52 | 62.7 | 0.9612 |
| Donor hypertension | 5 | 51 | 28.7 | 5 | 17 | 17.9 | 0 | 34 | 41.0 | 0.0007 |
| Positive donor CMV serology | 0 | 87 | 47.5 | 0 | 40 | 40.0 | 0 | 47 | 56.6 | 0.0249 |
| NA | m | SD | NA | m | SD | NA | m | SD | ||
| Recipient age (years) | 0 | 58.2 | 15.6 | 0 | 58.5 | 16.0 | 0 | 57.9 | 15.1 | 0.8069 |
| Donor age (years) | 1 | 59.7 | 17.3 | 1 | 60.3 | 17.0 | 0 | 59.0 | 17.6 | 0.7992 |
| Donor creatininemia (µmol/L) | 0 | 88.3 | 51.0 | 0 | 89.2 | 61.3 | 0 | 87.3 | 46.8 | 0.6285 |
| Duration on waiting list (months) | 0 | 22.0 | 20.3 | 0 | 21.9 | 21.6 | 0 | 22.1 | 18.6 | 0.9632 |
| Cold ischemia time (hours) | 0 | 13.3 | 5.6 | 0 | 12.7 | 5.8 | 0 | 13.9 | 5.1 | 0.1377 |
Description of the entire cohort according to induction therapy.
Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; CMV, cytomegalovirus; EBV, Epstein-Barr virus; ECD, expanded criteria donor; HLA, human leucocyte antigen; NA, not available (missing); sd, standard deviation; ESRD, end stage renal disease; PKD, polycystic kidney disease.
The average recipient age was 58.5 years in the BSX group versus 57.9 years in the ATG group (p = 0.80) and a majority of them were male (71.6%). 18% had a preemptive transplantation, 24.6% had history of diabetes and 61.2% received an allograft from an extended criteria donor (ECD) without any significant difference between groups. 41.2% of the recipients had a positive CMV serology (45.5% in the ATG group and 36.1% in the BSX group, p = 0.20) and 47.5% of the donors had a positive CMV serology (40.0% in the ATG group and 56.6% in the BSX group, p = 0.02).
With respect to steroid maintenance therapy, 31.1% of patients received corticotherapy by month 3 (32.8% in the BSX group and 29.7% in the ATG group, p = 0.67) with an average dose of 7 mg/day; and 38.8% at 1 year (38.9% in the BSX group and 38.8% in the ATG group, p = 0.16) with an average dose of 7 mg/day. Tacrolimus therapy was the most common immunosuppressant in both groups (95.8% vs. 94.0%, p = 0.72 at 3 months and 86.3% vs. 89.4%, p = 0.56 at 12 months in the BSX and ATG groups, respectively) with similar trough levels (8.3 ng/mL vs. 8.7 ng/mL at 3 months, p = 0.76 and 6.2 ng/mL vs. 6.7 ng/mL at 12 months, p = 0.19 in the BSX and ATG groups, respectively). Finally, the use of antiproliferative drugs was similar between patients who underwent an induction by BSX or ATG (respectively 87.6% vs. 92.8% at 3 months, p = 0.27 and 78.7% vs. 81.5% at 12 months, p = 0.67), Supplementary Figure S2.
Patient and Graft Survival
During the follow-up, 18 deaths with a functioning allograft (9 in each group) and 8 returns to dialysis (including 6 in the group BSX) were observed. Median event-free follow-up time was 3.0 years (min: 0.0; max: 5.2). The patient and graft survival, illustrated in Figure 2A, was 95% at 1-year post-transplantation (95% CI: 91%; 99%) in ATG group versus 94% in the BSX group (95% CI: 90%; 100%). These results corresponded to an adjusted HR of 1.22 (95% CI: 0.53; 2.80, p-value = 0.63), between patients of the BSX group versus those of the ATG group.
FIGURE 2
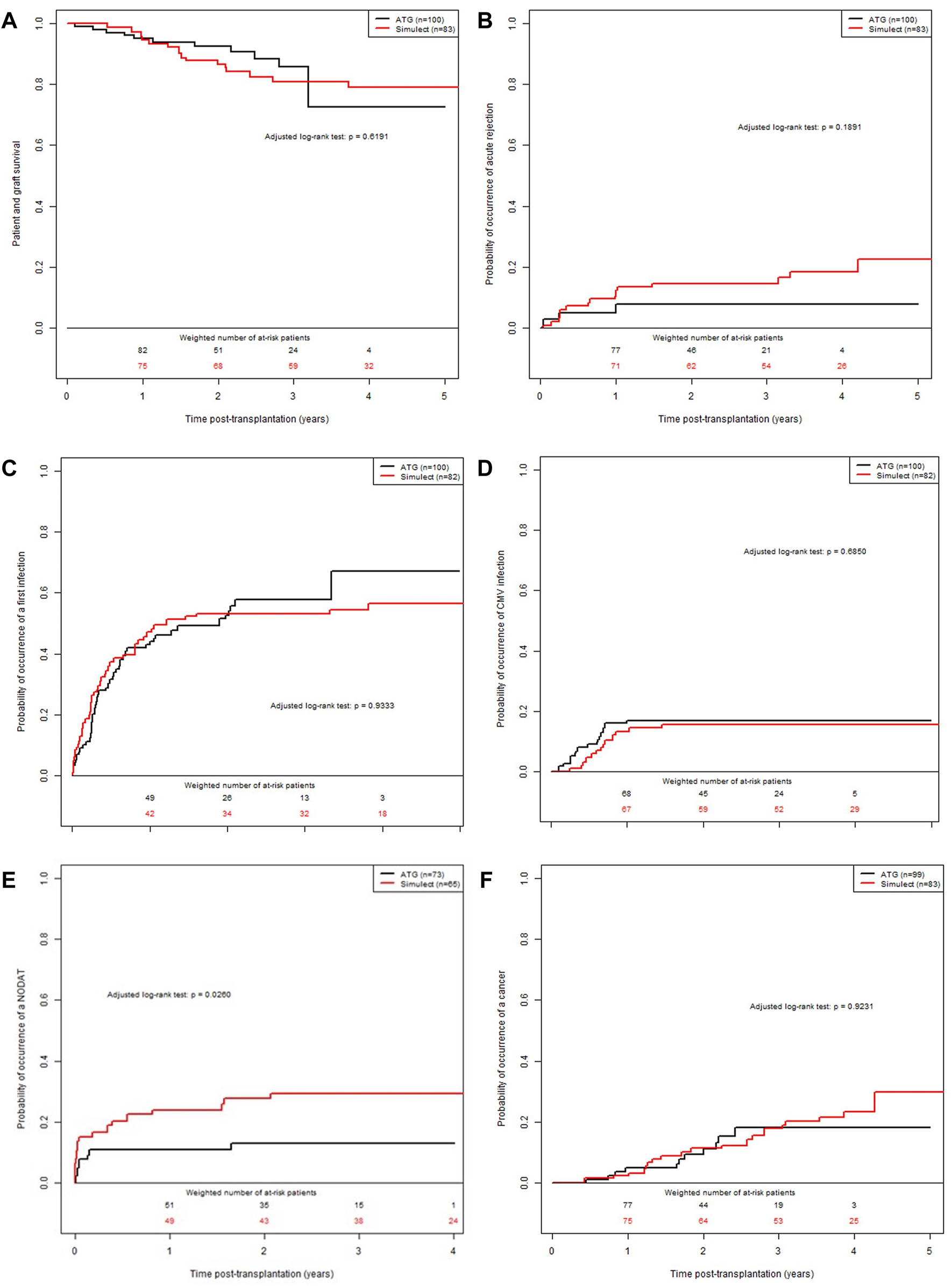
Confounder-adjusted probabilities of events according to the time post-transplantation and the induction therapy. (A) patient and graft survival. (B) cumulative probability of a first episode of acute rejection episode. (C) cumulative probability of infection. (D) cumulative probability of CMV replication. (E) cumulative probability of PTD. (F) cumulative probability of post-transplantation malignancy.
Occurrence of BPAR Episodes and dnDSA
The cumulative adjusted probabilities of the occurrence of a first BPAR is illustrated in Figure 2B. Median event-free follow-up time was 3.0 years (min: 0.0; max: 5.2). The value for the ATG group was 5% at 1-year post-transplantation (95% CI: 1%; 9%) versus 11% for the BSX group (95% CI: 4%; 17%). These results corresponded to an adjusted HR of 1.92 (95% CI: 0.77; 4.78, p-value = 0.15), between BSX patients compared to ATG treated patients. Finally, at 1-year post transplantation, 2 patients in the ATG group and 2 patients in the BSX group presented a DSA with MFI >1000. However, the MFI were rather lower in patients from the ATG group (2147 and 1441) compared to the BSX group (4,900 and 14,000).
During the follow-up, 279 biopsies were performed, 150 in the ATG group and 129 in the BSX group.
Overall, and considering all rejection episodes (first and recurrent), there was significantly more biopsies concluding to a BPAR in the BSX group (n = 22, representing 17.0% of performed biopsies) than in the ATG group (n = 11, representing 7.3% of performed biopsies), p = 0.0152, Supplementary Figure S3.
In the ATG group, BPAR consisted of 7 Borderline lesions (BL) and 4 T Cell Mediated Rejection (TCMR); these later were all successfully treated except for one patient who died with a functional allograft. Of note, among the 11 patients who presented a BPAR in the ATG group, 5 had a total dose < to 2 mg/kg and 6 a total dose > to 2 mg/kg.
In the BSX group, BPAR consisted of 11 BL, 8 TCMR, 1 Antibody Mediated Rejection (ABMR) and 2 mixed rejection (ABMR + TCMR). While 15 BPAR would have require a treatment, only 13 received it (2 patients were considered too frailty). 6 on 13 treated episodes evolved favorably, 6 were refractory and evolved towards end stage renal disease, and one patient deceased with a functional allograft.
Cumulative Probability of Infectious Complications
During the follow-up, 95 events (including 45 in the group BSX) were observed. Median event-free follow-up time was 3.0 years (min: 0.0; max: 5.0). The cumulative adjusted probabilities of the occurrence of infection is presented in Figure 2C. The value for the ATG group was 43% at 1-year post-transplantation (95% CI: 32%; 52%) versus 47% in the BSX group (95% CI: 35%; 57%). These results corresponded to an adjusted HR of 0.99 (95% CI: 0.65; 1.50, p-value = 0.95), between BSX patients versus ATG treated patients.
Cumulative Probability of CMV Viremia
During the follow-up, 30 events (including 14 in the group BSX) were observed. Median event-free follow-up time was 3.0 years (min: 0.0; max: 5.1). The cumulative adjusted probabilities of the occurrence of CMV viremia is presented in Figure 2D. The value for the ATG group was 17% at 1-year post-transplantation (95% CI: 9%; 24%) versus 13% for the BSX group (95% CI: 6%; 20%). These results corresponded to an adjusted HR of 0.85 (95% CI: 0.41; 1.78, p-value = 0.6731), between the two groups of patients.
Cumulative Probability of Post-Transplant Diabetes
The patient characteristics at the time of transplantation are presented in Supplementary Table S6. Among the 183 patients from the initial cohort, 45 were excluded because they were diabetic before transplantation, leading to a sub-cohort of 138 KTR: 65 patients were treated with BSX (47.1%) and 73 treated with ATG (52.9%). During the follow-up, 27 events were observed (including 18 of the BSX group). Median event-free follow-up time was 3.0 years (min: 0.4; max: 5.1). The cumulative adjusted probabilities of the occurrence of post-transplant diabetes is presented in Figure 2E. The value for the ATG group was 11% at 1-year post-transplantation (95% CI: 3%; 18%) versus 24% in the BSX group (95% CI: 13%; 34%). These results corresponded to an adjusted HR of 2.44 (95% CI: 1.09; 5.46, p-value = 0.03), between BSX versus ATG treated patients.
Cumulative Probability of Post-Transplant Malignancy
During the follow-up, 30 events were observed (19 in the group BSX). Median event-free follow-up time was 3.0 years (min: 0.0; max: 5.2). The cumulative adjusted probability of the occurrence of neoplastic (included squamous cell carcinoma and post-transplant lymphoma disease) is presented in Figure 2F. The value for the ATG group was 0.04 at 1-year post-transplantation (95% CI: 0.00; 0.08) versus 0.02 for the BSX group (95% CI: 0.00; 0.06). These results corresponded to an adjusted HR at 1.04 (95% CI: 0.48; 2.25, p-value = 0.9162), between BSX and ATG treated patient groups.
Evolution of Lymphocyte Count and Allograft Function
As expected, total lymphocyte counts were significantly lower during the first-year post-transplantation for patients in the ATG group (Figure 3A). However, after the sixth month post transplantation, the lymphocyte count in these patients increased, and the percentage of patients with severe lymphopenia (<750/mm3) decreased significantly (51.1% of patients receiving ATG had a severe lymphopenia at 6-month post transplantation vs. 28.0% at 9-month post transplantation, p = 0.01, Figure 3B). In the ATG group, patients who presented a severe lymphopenia at 1-year post-transplantation despite very low doses of thymoglobulin were significantly older (69 years old vs. 53 years old, p = 0.0020). Allograft function was globally similar between ATG and BSX groups, however with a trend to a better eGFR at 1-year post transplantation in patients from the ATG group (50.0 vs. 43.7 mL/min, p = 0.07), Figure 3C. Of note, there was no significant difference in the occurrence of delayed graft function between groups (26.2% vs. 29.2% in ATG and BSX groups respectively, p = 0.74).
FIGURE 3
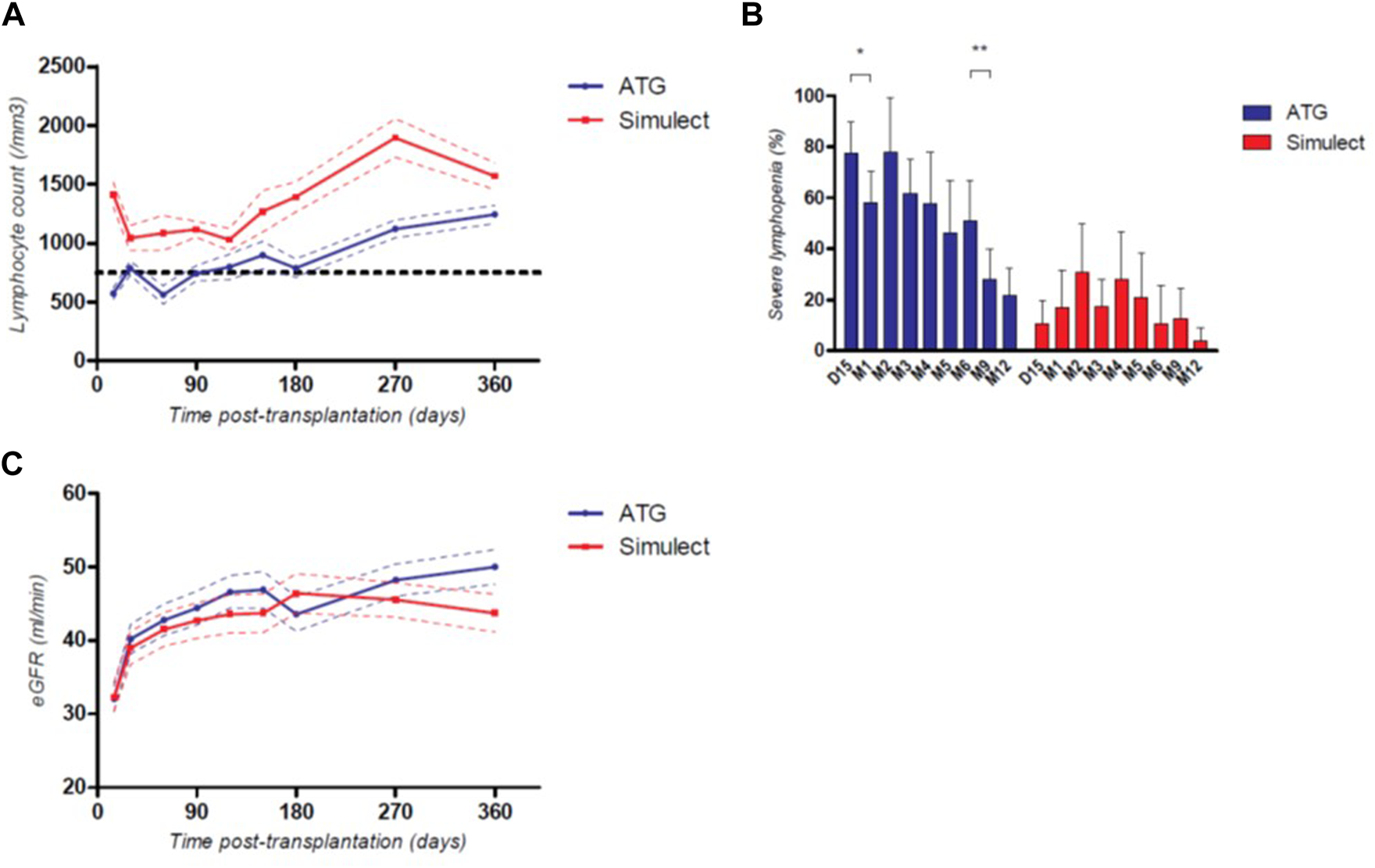
Mean total lymphocyte count (A), percentage of patients with severe lymphopenia (≤750/mm3) (B) and mean eGFR (C) during the first-year post transplantation depending on their induction therapy; *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01; continuous variables are represented with their respective standard mean error, categorical variables are represented with their respective 95CI%.
Discussion
Despite multiple studies characterizing induction therapy in low immunological risk kidney transplant recipients, controversies still exist regarding the best treatment to provide for these patients. Basiliximab is currently recommended by the KDIGO guidelines based on studies performed several years ago comparing BSX to ATG (4), notably because of an increased risk of viral infection due to the prolonged T cell depletion induced by ATG. However, as ATG acts in a dose-dependent manner (6), numerous transplant physicians have decreased its dosage over the years in order to reduce its side effects (17, 18).
We demonstrated the consequence of drastically reduced ATG dosage (average of 2 mg/kg total dose) in non-immunized recipients receiving a first kidney transplant, compared to basiliximab-treated patients, undergoing a similar maintenance therapy. Similarly, previous studies on smaller cohorts reported the safety of a very low dose of ATG in low immunological risk patients (19, 20). Other investigated outcomes related to a low dose of ATG, which however remained higher than our and usually associated with long term steroid therapy (21, 22). In relation to immunological complications, we found that a very low dose of ATG seems safe in this low-risk population with a comparable occurrence of a first episode of rejection. Moreover, we even observed a trend in favor of low doses of ATG. This non-significant difference was probably due to an underpowering of the study, and larger series seems mandatory to confirm this later point. Nevertheless, investigation of all BPAR episodes demonstrated a significant lower number of episodes rejection in patients from the very low ATG group. Moreover, patients from the ATG group had a significantly lower occurrence of post-transplant diabetes. One hypothesis is the different number of treated BPAR among groups, as steroids are known to promote post-transplant diabetes. Other reports evidenced a difference in PTD occurrence depending on the induction, but the exact imputability rather than the consecutive maintenance therapy management is still unclear (6, 23, 24). Finally, the small number of studied events may induce a lack of power and validation data from other cohorts will be of interest. Whilst ATG did not significantly impact allograft survival (1, 25), despite a trend to a better 1-year allograft function, it is well known that allograft rejection negatively impacts long-term kidney transplant outcomes (26, 27). Based on our data, a steroid-sparing strategy appears safe in low-immunological risk patients who received a very low dose of Thymoglobulin and can thus be conduce without increasing the risk of allograft rejection.
The use of ATG by transplant physicians is often accompanied by an apprehension of viral infections. In our cohort, according to a well-controlled prophylaxis, there was no significant difference between global infectious complications, nor CMV viremia, using low doses of ATG compared to an induction with Basiliximab. This is concordant with a previous study by our group where we found no difference in infectious complications (notably CMV viremia) regarding ATG administration in elderly kidney transplant recipients (6). Indeed, CMV viremia may be more related to the presence—or not—of the specific CMV cellular immunity rather than the total lymphocyte count (28).
Obviously, the use of ATG resulted in deep lymphopenia in the first months’ post-transplantation. However, the reduced dosage in our cohort led to a higher lymphocyte count at 1-year post transplantation than previously described (29). Moreover, after the sixth month post transplantation, the percentage of patients presenting a severe lymphopenia, which is known to impact patient survival (30), significantly decreased. This shorter time of deep lymphopenia may enhance the use of ATG at a very low dosage in non-immunized kidney transplant recipients, particularly in younger recipients.
Finally, the use of ATG at this very low dose also seemed to permit cost savings for our institution. In France, induction by Simulect® costs around 3,000 euros per patient and 25 mg of thymoglobulin costs around 250 euros. In our cohort, induction by ATG despite basiliximab for non-immunized patients permitted a total saving of 150,000 euros in 5 years (1,500 euros per patient). These results differs from others who found a cost saving using Basiliximab, because the highest dosage of ATG induced more infectious complications (31). However, as we did not perform a cost-effectiveness study assessing all cumulative costs (days of hospitalization, number of consultations, post-transplant complications … ), definitive conclusions are not possible. A recent American cost-effectiveness study revealed that use of ATG appeared to offer cost and outcomes advantages compared to no-induction in kidney transplant recipients (32).
Our study has some limitations, the main one being the relatively small monocentric sample size, with requirement of further validation, ideally based on a randomized clinical trial which remains the gold standard. However, retrospective data from other centers could not have been included as their total ATG dose is considerably higher. Also, based on recent improvements in detecting anti-HLA immunogenicity, determination of low-risk kidney transplant recipients (i.e., total absence of significant anti-HLA antibodies) is now more accurate, and some transplant teams are currently conducting clinical trials to assess the benefit of induction therapy in this low-risk population (33). In our cohort, ATG induced a better prevention of BPAR than Basiliximab, which supports the pursuit of induction therapy for these patients; which however needs to be tailored to provide a very low dose of ATG.
In conclusion, our report highlights that a very low dose of ATG in non-immunized recipients was safe and associated with a lower rate of rejection episodes and post-transplant diabetes, without increasing infectious complications probably because of a reduced duration of deep lymphopenia.
Nantes DIVAT Consortium
Gilles Blancho, Julien Branchereau, Diego Cantarovich, Anne Cesbron, Agnès Chapelet, Jacques Dantal, Florent Delbos, Clément Deltombe, Anne Devis, Lucile Figueres, Raphael Gaisne, Claire Garandeau, Magali Giral, Caroline Gourraud-Vercel, Maryvonne Hourmant, Christine Kandel-Aznar, Georges Karam, Clarisse Kerleau, Delphine Kervella, Alice Leclech, Claire Leman, Christophe Masset, Aurélie Meurette, Karine Renaudin, Simon Ville, Alexandre Walencik.
Statements
Data availability statement
Complete datasets are available upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
CM: collected the data, participated in the study analysis, and wrote the manuscript. CK: participated in the study analysis. JD: elaborated design and research project, supervised analysis, and critically revised the manuscript. AW: participated in collection and analysis of data, significantly participated in the reviewing process and approved the final version of the manuscript. All authors participated in writing and revising the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded using institutional grants dedicated to the DIVAT database and industrial donation from Sanofi. The authors declare that this study received funding from Sanofi. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article or the decision to submit it for publication.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the physicians who helped recruit patients and all patients who participated in this study. We also thank the clinical research associates who participated in the data collection.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontierspartnerships.org/articles/10.3389/ti.2023.10816/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
95%CI, 95% Confidence Interval; ATG, anti-thymocyte globulins; BMI, body mass index; BPAR, biopsy proven acute rejection; BSX, basiliximab; CIT, cold ischemia time; CMV, cytomegalovirus; CNI, calcineurin inhibitors; DGF, delayed graft function; DSA, donor-specific antibodies; ECD, expanded criteria donor; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HLA, human leucocyte antigen; HR, hazard ratio; KDIGO, kidney disease improving global outcomes; MMF, mycophenolate mofetil; MPA, mycophenolic acid; OR, odds-ratio; SCr, serum creatinine; sd, standard deviation; RMST, restricted mean survival time; RMTL, restricted mean time lost.
References
1.
Webster AC Ruster LP McGee R Matheson SL Higgins GY Willis NS et al Interleukin 2 Receptor Antagonists for Kidney Transplant Recipients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (2010) 1:CD003897. 10.1002/14651858.CD003897.pub3
2.
Noel C Abramowicz D Durand D Mourad G Lang P Kessler M et al Daclizumab versus Antithymocyte Globulin in High-Immunological-Risk Renal Transplant Recipients. J Am Soc Nephrol (2009) 20:1385–92. 10.1681/ASN.2008101037
3.
Brennan DC Daller JA Lake KD Cibrik D Del Castillo D Thymoglobulin Induction Study Group. Rabbit Antithymocyte Globulin versus Basiliximab in Renal Transplantation. N Engl J Med (2006) 355:19671977–7. 10.1056/NEJMoa060068
4.
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Transplant Work Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for the Care of Kidney Transplant Recipients. Am J Transpl (2009) 9(3):S1–155. 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2009.02834.x
5.
Chappell D Beiras-Fernandez A Hammer C Thein E . In Vivo visualization of the Effect of Polyclonal Antithymocyte Globulins on the Microcirculation after Ischemia/reperfusion in a Primate Model. Transplantation (2006) 81:552–8. 10.1097/01.tp.0000200305.48244.a6
6.
Masset C Boucquemont J Garandeau C Buron F Morelon E Girerd S et al Induction Therapy in Elderly Kidney Transplant Recipients with Low Immunological Risk. Transplantation (2020) 104:613622–2. 10.1097/TP.0000000000002804
7.
Thomusch O Wiesener M Opgenoorth M Pascher A Woitas RP Witzke O et al Rabbit-ATG or Basiliximab Induction for Rapid Steroid Withdrawal after Renal Transplantation (Harmony): an Open-Label, Multicentre, Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet (2016) 388:3006–16. 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32187-0
8.
Büchler M Longuet H Lemoine R Herr F Gatault P Thibault G et al Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Studies of Two Different Rabbit Antithymocyte Globulin Dosing Regimens: Results of a Randomized Trial. Transpl Immunol (2013) 28:120–6. 10.1016/j.trim.2013.03.001
9.
Loupy A Haas M Roufosse C Naesens M Adam B Afrouzian M et al The Banff 2019 Kidney Meeting Report (I): Updates on and Clarification of Criteria for T Cell– and Antibody Mediated Rejection. Am J Transpl (2020) 20:2318–31. 10.1111/ajt.15898
10.
Austin PC . The Performance of Different Propensity-Score Methods for Estimating Differences in Proportions (Risk Differences or Absolute Risk Reductions) in Observational Studies. Stat Med (2010) 29:2137–48. 10.1002/sim.3854
11.
Rosenbaum PR Rubin DB . The central Role of the Propensity Score in Observational Studies for Causal Effects. Biometrika (1983) 70:41–55. 10.1093/biomet/70.1.41
12.
Robins JM Hernán MA Brumback B . Marginal Structural Models and Causal Inference in Epidemiology. Epidemiology (2000) 11:550–60. 10.1097/00001648-200009000-00011
13.
Xie J Liu C . Adjusted Kaplan-Meier Estimator and Log-Rank Test with Inverse Probability of Treatment Weighting for Survival Data. Stat Med (2005) 24:3089–110. 10.1002/sim.2174
14.
Lin DY Wei LJ . The Robust Inference for the Cox Proportional Hazards Model. J Am Stat Assoc (1989) 84:1074–8. 10.1080/01621459.1989.10478874
15.
R Development Core Team, . R : A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. (2010).
16.
Najarian JS Fryd DS Ferguson RM. Seven Years’ Experience with Antilymphoblast Globulin for Renal Transplantation from Cadaver Donors. 16.
17.
Boucquemont J Foucher Y Masset C Legendre C Scemla A Buron F et al Induction Therapy in Kidney Transplant Recipients: Description of the Practices According to the Calendar Period from the French Multicentric DIVAT Cohort. PLoS ONE (2020) 15:e0240929. 10.1371/journal.pone.0240929
18.
Gurk-Turner C Airee R Philosophe B Kukuruga D Drachenberg C Haririan A . Thymoglobulin Dose Optimization for Induction Therapy in High Risk Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transplantation (2008) 85:1425–30. 10.1097/TP.0b013e31816dd596
19.
Schenker P Ozturk A Vonend O Kruger B Jazra M Wunsch A et al Single-dose Thymoglobulin Induction in Living-Donor Renal Transplantation. Ann Transpl (2011) 16:50–8. 10.12659/aot.881865
20.
Kho MML Bouvy AP Cadogan M Kraaijeveld R Baan CC Weimar W . The Effect of Low and Ultra-low Dosages Thymoglobulin on Peripheral T, B and NK Cells in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transpl Immunol (2012) 26:186–90. 10.1016/j.trim.2012.02.003
21.
Jalalonmuhali M Ng KP Ong CS Lee YW Wan Md Adnan WAH Lim SK . Low Immunologic Risk Living Related Renal Transplant Using Very Low-Dose Antithymocyte Globulin as Induction Therapy: A Single Tertiary Hospital Experience. Transplant Proc (2020) 52:1709–14. 10.1016/j.transproceed.2020.02.139
22.
Martinez-Mier G Moreno-Ley PI Budar-Fernandez LF Mendez-Lopez MT Allende-Castellanos CA Jimenez-Lopez LA et al Low-dose Thymoglobulin vs Basiliximab Induction Therapy in Low-Risk Living Related Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Prospective Randomized Trial. Transplant Proc (2021) 53:1005–9. 10.1016/j.transproceed.2020.01.054
23.
Bayés B Pastor MC Lauzurica R Granada ML Salinas I Romero R . Do Anti-CD25 Monoclonal Antibodies Potentiate Posttransplant Diabetes Mellitus?Transplant Proc (2007) 39:2248–50. 10.1016/j.transproceed.2007.06.021
24.
Prasad N Gurjer D Bhadauria D Gupta A Srivastava A Kaul A et al Is Basiliximab Induction, a Novel Risk Factor for New Onset Diabetes after Transplantation for Living Donor Renal Allograft Recipients?: NODAT with Basiliximab Induction. Nephrology (2014) 19:244–50. 10.1111/nep.12209
25.
Bamoulid J Staeck O Crepin T Halleck F Saas P Brakemeier S et al Anti-thymocyte Globulins in Kidney Transplantation: Focus on Current Indications and Long-Term Immunological Side Effects. Nephrol Dial Transpl (2016) gfw368:1601–8. 10.1093/ndt/gfw368
26.
Rampersad C Balshaw R Gibson IW Ho J Shaw J Karpinski M et al The Negative Impact of T Cell–Mediated Rejection on Renal Allograft Survival in the Modern Era. Am J Transplant (2022) 22:761–71. 10.1111/ajt.16883
27.
Chandran S Mannon RB . T Cell–Mediated Rejection in Kidney Transplant Recipients: The end(point) Is Also the Beginning. Am J Transplant (2022) 22:683–4. 10.1111/ajt.16964
28.
Jarque M Melilli E Crespo E Manonelles A Montero N Torras J et al CMV-Specific Cell-Mediated Immunity at 3-month Prophylaxis Withdrawal Discriminates D+/R+ Kidney Transplants at Risk of Late-Onset CMV Infection Regardless the Type of Induction Therapy. Transplantation (2018) 102:e472–80. 10.1097/TP.0000000000002421
29.
Longuet H Sautenet B Gatault P Thibault G Barbet C Marliere JF et al Risk Factors for Impaired CD 4 + T‐cell Reconstitution Following Rabbit Antithymocyte Globulin Treatment in Kidney Transplantation. Transpl Int (2014) 27:271–9. 10.1111/tri.12249
30.
Dujardin A Lorent M Foucher Y Legendre C Kerleau C Brouard S et al Time-dependent Lymphocyte Count after Transplantation Is Associated with Higher Risk of Graft Failure and Death. Kidney Int (2021) 99:1189–201. 10.1016/j.kint.2020.08.010
31.
Lilliu H Brun-Strang C Le Pen C Buchler M Al NajjAr A Priol G et al Cost-minimization Study Comparing Simulect ® vs. Thymoglobulin® in Renal Transplant Induction. Clin Transplant (2004) 18:247253–3. 10.1111/j.1399-0012.2004.00148.x
32.
Gharibi Z Ayvaci MUS Hahsler M Giacoma T Gaston RS Tanriover B . Cost-Effectiveness of Antibody-Based Induction Therapy in Deceased Donor Kidney Transplantation in the United States. Transplantation (2017) 101:12341241–1. 10.1097/TP.0000000000001310
33.
Ajlan A . Standard Induction with Basiliximab versus No-Induction in Low Immunological Risk Kidney Transplant Recipients - Prospective Randomized Double Blind Controlled Clinical Trial (2021). Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04404127.
Summary
Keywords
diabetes mellitus, rejection, induction therapy, low immunological risk, low dose thymoglobulin
Citation
Masset C, Kerleau C, Blancho G, Hourmant M, Walencik A, Ville S, Kervella D, Cantarovich D, Houzet A, Giral M, Garandeau C, Dantal J and the Nantes DIVAT Consortium (2023) Very Low Dose Anti-Thymocyte Globulins Versus Basiliximab in Non-Immunized Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transpl Int 36:10816. doi: 10.3389/ti.2023.10816
Received
03 August 2022
Accepted
19 January 2023
Published
03 February 2023
Volume
36 - 2023
Updates
Copyright
© 2023 Masset, Kerleau, Blancho, Hourmant, Walencik, Ville, Kervella, Cantarovich, Houzet, Giral, Garandeau, Dantal and the Nantes DIVAT Consortium.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Christophe Masset, christophe.masset@chu-nantes.fr
Données Informatisées et VAlidées en Transplantation, DIVAT Cohort Collaborators (Medical Doctors, Surgeons, HLA Biologists) are listed at the end of the article
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.