Abstract
Pregnancy after solid organ transplantation (SOT) has potential risks for the offspring. Most existing research focused on short-term pregnancy outcomes. The aim of this systematic review was to evaluate available data concerning longer term outcomes (>1 year) of these children. A systematic literature search, following PRISMA guidelines, of PubMed and Embase was performed from the earliest date of inception through to 6th April 2022. Publications on all types of (combined) SOT were eligible for inclusion. In total, 53 articles were included. The majority assessed offspring after kidney (78% of offspring) or liver transplantation (17% of offspring). 33 studies included offspring aged >4 years and five offspring aged >18 years. One study was included on fathers with SOT. The majority of the 1,664 included children after maternal SOT had normal intellectual, psychomotor, and behavioral development. Although prematurity and low birth weight were commonly present, regular growth after 1 year of age was described. No studies reported opportunistic or chronic infections or abnormal response to vaccinations. In general, pregnancy after SOT appears to have reassuring longer term outcomes for the offspring. However, existing information is predominantly limited to studies with young children. Longer prospective studies with follow-up into adulthood of these children are warranted.

Introduction
Solid organ transplantations (SOT) are increasingly performed worldwide. Pregnancy numbers after SOT have increased. Over 3,200 pregnancies after maternal SOT have been described in the Transplant Pregnancy Registry International (TPRI) database (1). SOT pregnancies are associated with increased incidence of prematurity and low birth weight (LBW) (1–3). All pregnancies after SOT are classified as high risk (1), but risk differs per SOT. The most severe risk is seen after heart and lung transplantation (HTx, LuTx) (1). However, after kidney and liver transplantation (KTx, LiTx), live birth rate and miscarriage rates are reported to be similar to the general population (3–5), and the majority of offspring in SOT pregnancies are reported as healthy at birth (1–4). Most data on the offspring only focused on perinatal outcomes such as prematurity, birth weight, congenital abnormalities, congenital infections, and APGAR scores. A recent overview on post-transplant pregnancy by Klein et al. emphasized the lack of available data on the long-term health of the offspring (6). To the best of our knowledge, no systematic review on longer term outcomes after birth of the offspring born after SOT exists. Therefore, the aim of this systematic review is to evaluate the available data concerning longer term outcomes (>1 year) of children of SOT patients.
Materials and Methods
Data Sources and Searches
A systematic literature search, made in consultation with an information specialist, of PubMed and Embase was performed, from the earliest date of inception through to 6th April 2022. A protocol for the systematic review was prepared locally but not submitted or registered online. The following key terms and their synonyms were used: organ transplantation (with all SOT transplants: heart, lung, kidney, liver, pancreas and small bowel separately mentioned), pregnancy, child. A reproducible search strategy is provided in Supplementary Table S1.
Study Selection
All pregnancies with either a mother or father with a SOT (heart, lung, kidney, liver, pancreas, or small bowel) as well as combined SOT in their history were eligible for inclusion. Articles were included if >1-year follow-up data of the offspring was described. In overlapping articles, the most recent article was included. Articles not written in English, conference abstracts, (systematic) reviews, and meta-analysis were excluded.
Initial selection based on title and abstract was performed by two researchers (JRM and MFC) independently. All disagreements were discussed and, if there was doubt, the study was included for full-text screening, performed by the same two researchers. All discrepancies during full-text screening were resolved by consensus by the same two researchers. All citations of eligible articles and relevant review articles were consulted for Supplementary References. Two articles were identified that were not found in the primary search. The PRISMA (preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analyses) flowchart (7) was used to document the number of articles included and excluded, including the rationale for exclusion (Figure 1).
FIGURE 1
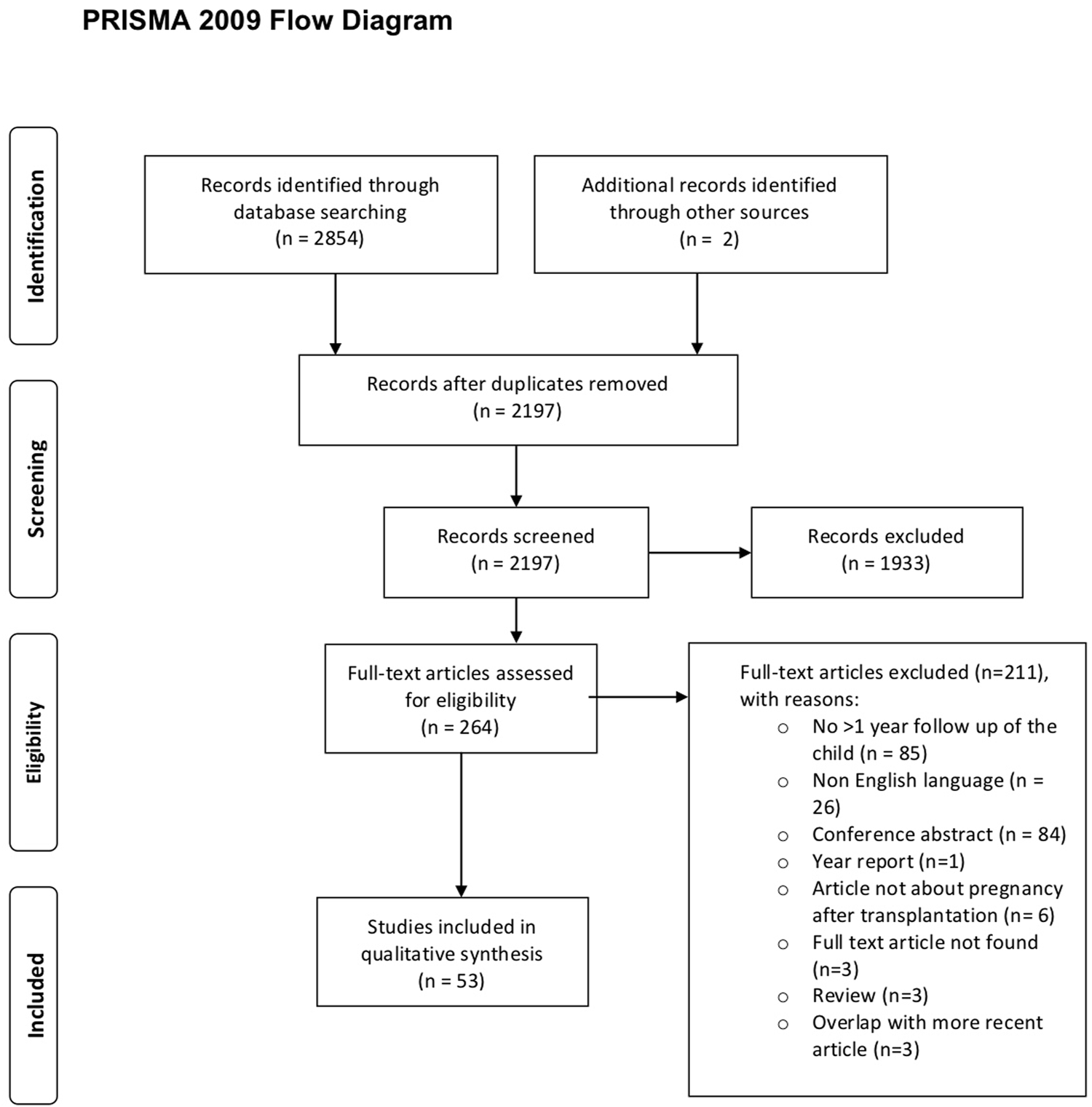
PRISMA flow diagram study inclusion.
Data Extraction
Data extraction was carried out by one researcher (JRM). A second researcher (MFC) independently performed a full-text check for accuracy and completeness. All discrepancies were resolved by consensus of the authors. For each included study the following data was extracted and summarized in two tables: first author, country, study type, follow-up period, number of live births, transplanted organ, immunosuppressive regimen, mean/median birth weight, mean/median gestational age, method of assessment, and the longer-term outcomes. All longer-term outcomes were evaluated, with specific attention for growth, immunological, neurocognitive, and behavioral follow-up and kidney function. Data on intra uterine fetal deaths and miscarriages were not included. Authors of primary studies were not contacted to provide missing data. Biased appraisal of the articles was performed by two researchers (JRM and JRP) (Supplementary Tables S2A,S2B). For prospective and retrospective cohort studies we used the Newcastle Ottawa Scale (NOS) for cohort studies (8). For cross-sectional studies and case reports we used the applicable Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) critical appraisal checklists (9).
Definitions
The following definitions were used: preterm: <37 weeks of gestation, LBW: <2,500 g, and catch-up growth: rapid growth in children following a period of reduced growth (10).
Results
The systematic search yielded 2,854 articles. 657 were duplicates (Figure 1). After full text screening (n = 264), n = 53 articles were selected (Tables 1, 2; Supplementary Tables S2A,S2B), yielding 19 case reports, 18 retrospective, 10 prospective, and six cross-sectional cohort studies. In 16 studies a comparison with a control group was made, whereby the control group was matched in 12 studies. In 13 articles, pregnancies after multiple SOT types were assessed, leading to 36 articles assessing offspring born after KTx, 16 after LiTx, three after combined pancreas-kidney transplantation, seven after HTx, one after LuTx, and one after combined heart-lung transplantation. No article about offspring born after small bowel transplantation was found. One study on children from fathers with SOT was found (11). The majority of the studies (n = 33 (62%)) reported results on children with a follow-up of >4 years. Of these, twelve reported on children aged up to 8 years and eight on children aged up to 12 years. Follow-up on children aged up to 18 years was reported in eight studies and in five studies, children above the age of 18 were included (Tables 1, 2). Paragraphs 3.1–3.6 describe the offspring born to mothers with a SOT; paragraph 3.7 describes the offspring born to a father with a SOT.
TABLE 1
| Author (Year), country | Transplanted organ, number of children | Follow-up age children | Outcome measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Devresse (2022), Belgium (13) | Kidney: 43 infants (2 twins) from 32 women (57 pregnancies), 48% female | Median follow-up 17 years (range 7–25) | • Questionnaire sent to 43 children or their parents if < 18 years. 21 responded. Questions on current situation (weight, height, familial status, and treatment), medical history (hypertension, diabetes, and depression), addictions (smoking, etc.) and education |
| Egerup (2021), Denmark (49) | Kidney: 124 infants | Median follow-up 14.5 years [IQR 7.1–22.8] | • Administrative codes of diagnosis and antibiotic prescriptions identified in national registries |
| Control: 1,231 infants | Median follow-up control group 14.1 years IQR 6.6–25.4] | ||
| Borek-Dziecioł (2020), Poland (58) | Kidney: 40 infants | Newborns, infants, and children over 1 year of age were examined. Not described at what age | • Renal parameters: urea, creatinine, potassium, and sodium concentration were analyzed |
| Control: 40 infants | |||
| Dębska-Slizien (2020), Poland (26) | Kidney: 25 infants | Median follow-up 9 years (range 0.5–30 years) | • No specific long-term outcomes described |
| Bachmann (2019), Germany (40) | Kidney: 30 infants | Follow-up at birth, 12 and 24 months 65.6% of the children had a complete dataset at 24 months | • Physical and psychomotor development examination by a pediatrician, collected from the patient file (weight, length, and head circumference) |
| Combined kidney-pancreas: 2 infants | • Questionnaire filled in by the mother about the child (physical examination, anthropometric measures, medical, and paramedical history) | ||
| Morales-Buenrostro (2019), Mexico (50) | Kidney: 50 infants | Children >4 years were included. Most children were aged between 6 and 16 years (n = 32 in the study group and n = 37 in the control group) | • Interview with the mother and the child |
| Control: 50 infants | • Intellectual performance: IQ scores (age-specific test: WPPSI, WISC-IV, WAIS-III) | ||
| Schreiber-Zamora (2019), Poland (1) (51) | Kidney: 36 infants | Follow-up at one time-point, median 3.12 years | • Age-specific neurological examination including ultrasound |
| Control: 36 infants | |||
| Schreiber-Zamora (2019), Poland (2) (42) | Liver: 35 infants | Follow-up Tx group: 6 children 1–12 months, 15 children 1–3 years, 25 children 3–6 years, 15 children >6 years | • Measurement of BMI as a one-time measurement |
| Kidney: 26 infants | Follow-up control group: 7 children 1–12 months, 16 children 1–3 years, 24 3–6 years, 17 children >6 years | ||
| Control: 64 infants | |||
| Turkyilmaz (2018), Turkey (14) | Liver: 8 infants | Mean follow-up 3.2 years ± 2.4 years, range 1–7 years | • Retrospective analyses of patient records, no specific long term outcome measurements described |
| Kociszewska-Najman (2018), Poland (52) | Liver: 42 infants | 1 assessment per child (n = 31 < 30 months, n = 47 > 30 months) | • Psychological examination performed by qualified clinical psychologists. Results expressed in IQ (age specific tests: Psyche Cattell Infant Intelligence Scale, Terman-Merril Intelligence Scale, Scales of Raven’s Progressive Matrices) |
| Kidney: 38 infants | |||
| Control: 78 infants | |||
| Ono (2015), Brazil (44) | Kidney: 28 infants (1 twin) | Immunological follow-up at birth and at 8 months of age. General follow-up by the pediatrician every month during the first 6 months, every 3 months until 2 years of age | • Blood sample collection at birth from the umbilical cord and at 8 months from a peripheral vein. Immuno-phenotypic studies were done with fresh blood. Each sample was stained with fluorochrome-conjugated monoclonal antibodies |
| Control group 1: 40 infants | • Factors associated with hospital admission were analyzed by univariate logistic regression | ||
| Control group 2: 28 infants | |||
| Czaplinska (2014), Poland (60) | Liver: 51 infants | Neonates, infants, and children >1 year of age were examined. Not described at what age | • Analysis of liver parameters: alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) and two kidney parameters (urea and creatinine) |
| Control: 51 infants | |||
| Norrman (2014), Sweden (61) | Kidney | Group 1: mean age at follow-up: 9.7 ± 4.2 years | • Retrospective analyses of 5 registries: National Quality Register of Assisted Reproduction, the National Register in IVF, the Swedish Medical Birth Register, the National Patient Register, and the Swedish Cause of Death Register |
| Group 1: 7 infants (1 twin) | Group 2: mean age of follow-up: 14.7 ± 9.4 years | ||
| Group 2: 199 infants | |||
| Control | |||
| Group 3: 665 infants | |||
| Group 4: 3,980 infants | |||
| Drozdowska-Szymczak (2014), Poland (48) | Kidney: 39 infants | Follow-up at 1 time-point, range: 1 day-15 years (n = 26 > 10 months) and in the control group 1 day till 14 years | • Serum IgG and IgM measurements at 1 time-point with agglutination immunoassays |
| Control: 39 infants | |||
| Kociszewska-Najman (2013), Poland (62) | Liver: 37 infants | Follow-up: neonatal (1–4 weeks of age), babyhood (2–12 months), early kindergarten (1–3 years), later kindergarten (4–6 years) and school years (>6 years). Not all children at all follow-up moments tested. Most children tested in the late kindergarten stage | • Retrospective analyses of the parameters in the neonatal period of the child |
| Kidney: 45 infants | • Prospective ophthalmological examinations by a pediatric ophthalmologist | ||
| Control: 66 infants | |||
| Shaner (2012), United States (16) | Lung: 18 infants (1 triplet) | Follow-up mean: 7.0 years (± 5.37), range: 1.25 till 17.36 years | • NTPR registry and retrospective questionnaires, no specific long-term outcomes described |
| Nulman (2010), Canada (30) | Kidney: 39 infants | Mean follow-up 8.06 years, range: 3 years 7 months till 15 years 9 months | • Physical examination of the child (weight, length, and head circumference) |
| Control: 38 infants | • Psychological examination of mother and child conducted by a trained psychologic assistant under supervision of a registered psychologist | ||
| • Child: IQ: WPPSI-R, Visuomotor abilities: VMI-4 and the WRAVMA. | |||
| Al-Khader (2004), Saudi-Arabia (12) | Kidney: 110 infants (3 twins) | Follow-up of 41 infants, mean follow-up: 52 months (range: 13–83 months) | • Retrospective analyses of medical records including laboratory measurements, no details on the method of follow-up mentioned |
| Miniero (2004), Italy (18) | Kidney: 52 infants | Follow-up ranging from 2 months till 13 years | • Retrospective questionnaires, patient record data, and interviews in person or by telephone (growth, vaccinations, allergic reactions, diseases, laboratory tests, and last measured height and weight) |
| Liver: 7 infants | |||
| Heart: 8 infants (1 twin) | |||
| Bar (2003), Israel (63) | Kidney: 48 infants | Follow-up 2–7 years | • Retrospective analyses of medical records (short-term outcomes e.g., caesarean delivery, hospitalization, stillbirths) |
| Control: 48 infants | • Blinded periodical examination up to 7 years (maternal renal function, infant status, presence of severe handicap) | ||
| Sgro (2002), Canada (31) | Kidney: 32 infants | Follow-up mean 3.1 year (range 3 months till 11 years) | • Retrospective analyses of medical records |
| Control: 88 infants | • Pediatric follow-up visit: physical examination including growth parameters, neurodevelopmental assessment (Denver Developmental Screening test) | ||
| Giudice (2000), France (32) | Kidney: 10 infants (1 twin) | Follow-up of 12 children at 2.6 ± 1.8 years (range 1.0–6.9 years) | • Renal function tests (blood pressure, inulin clearance, paraminohippuric acid clearance, microalbuminuria, electrolyte reabsorption rate, renal ultrasound including renal size) |
| Pancreas-kidney: 1 infant | • Retrospective neonatal history | ||
| Heart: 2 infants | • Complete physical examination at the time of the renal function study | ||
| Liver: 1 infant | |||
| Willis (2000), United Kingdom (33) | Kidney: 48 infants (1 triplet) | Median follow-up: 5.2 years (range 9 months–18 years) | • Surveys, semi-structured interviews, medical records, and physical examination carried out by a researcher (blood pressure, developmental milestones, scholastic and educational achievements, urine sample, ultrasound examination of the urinary tract) |
| Stanley (1999), United States (56) | Kidney: 175 infants (52% girls) | Range of the child’s age at interview: 4 months-12 years, mean age: 4.4 years | • Assessment of developmental status (≤5 years: Child Development Review system, >5 years: prior developmental or present educational morbidity reported by the mother) |
| McGrory (1998), United States (19) | Combined pancreas -kidney and 1 pancreas followed by kidney: 20 infants | Follow-up ranging from 1 month to 8 years | • Data collected from a questionnaire, medical records, and telephone interviews. No specific long-term outcome measurements |
| Wu (1998), Germany (34) | Liver: 23 infants (1 twin) | Follow-up range 1–99 months 5 children <1 year at last follow-up | • Data obtained via medical records and questionnaires evaluated by the pediatrician (height and weight, psychological development, neurological development) |
| Jain (1997), United States (35) | Liver: 27 infants (long-term follow-up n = 25) | Multiple, frequency and timing not specified, follow-up moments. Median follow-up of 39 months (range 10–76 months) | • Prospectively collected data by patients, obstetricians, and the physicians. Weight for age percentiles calculated from the National Center for Health Statistics percentiles |
| Wong (1995), New-Zealand (55) | Kidney: 11 infants | Follow-up ranging from 15 months to 18 years | • Retrospective information from medical records (clinical and laboratory data, physical growth, physical examination, school performance, work achievement, social behavior, developmental milestones tested with the Denver developmental screening test) |
| Pilarski (1994), Canada (45) | Kidney: 11 infants | 1 follow-up per infant. Follow-up time ranging from 5 months till 9 years (1 child <1 year at follow-up) | • Immunological assessment of blood samples |
| Liver: 1 infant | |||
| Pahl (1993), United States (43) | Kidney: 26 infants | Mean follow-up: 5 years, range: 1 week - 18 years (5 children <1 year) | • Analyses of medical records (mother and child if present), interviews with the physician, interviews of the mothers by telephone or email (childhood development of their child (ren)) |
| Shaheen (1993), Saudi Arabia (59) | Kidney: 26 infants | Mean follow-up 39 months (range 6–72 months) | • Basic tests of kidney function and integrity on 22 children |
| • Serum cyclosporine was measured in whole blood using radioimmunoassays | |||
| Wagoner (1993), United States (25) | Heart: 28 infants | Mean follow-up 3.4 years (range 3 months till 6.5 years) | • Questionnaires study: no specific long-term outcome measurements described |
| Heart and lung: 3 infants | |||
| Rasmussen (1981), Sweden (47) | Kidney: 5 infants | Follow-up ranging from 4.5 to 9 years. Follow-up frequency between 2 and 4 times | • Somatic and psychomotor evaluation at regular intervals |
| • Immunological follow-up from peripheral blood at multiple time points: % rosette-forming PBM’s, proliferative responses of PBM to phythemagglutinin and pokeweed mitogen, counting the PBMs with surface immunoglobulins using fluoresceinated anti-light chain antisera, quantitative immunoglobulin levels for IgG, IgA and IgM, serum testing for antibodies against hepatitis B, polio virus, Haemophilus influenza, and Escherichia coli. Serum aspartate transferase and alanine transferase in HBsAg-positive children | |||
| • Chromosomal analyses performed in 4 children | |||
| Korsch (1980), United States (11) | Fathers with a kidney Tx: 4 infants (0 girls) from 3 fathers | Follow-up: ranging from 4 months to 6 years and 8 months (father KT: 4 months, 10 months, 11 months, 2 years 7 months and mother KT: 7 months, 1 year, 1 year 10 months, 2 years 4 months, 3 years 2 months, 6 years 8 months) | • Patient records, physical examination by a pediatrician |
| Mothers with a kidney Tx: 6 infants (2 girls) in 5 women | • Developmental evaluations on nine of the children by a specialist in assessing child development (age specific: Stanford-Binet test, Gesell Developmental Schedules, and Bayley Scales of Infant Development) | ||
| • A semi-structured interview by a social work assistant trained in sociologic research methods on the parents’ attitudes about their child’s development |
Included studies, cohort studies.
TABLE 2
| Author (Year), country | Transplanted organ, number of children | Follow-up age children | Outcome measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rao (2019), Australia (41) | Kidney: 1 infant | Follow-up 2 years | • The weight of the infant was followed up for 2 years |
| Mahmoud (2017), Kuwait (15) | Kidney: 4 infants (1 triplet) | Follow-up at birth, discharge, 12 months and 24 months | • No specific outcome measurements described |
| Kociszewska-Najman (2012), Poland (29) | Liver: 2 infants | 1 infant: follow-up visit at 7 months 1 child follow-up visit at 21 months | • Length, weight, head circumference, blood pressure, laboratory tests, abdominal ultrasound, and echocardiogram |
| • Neurodevelopmental and socio-emotional assessment | |||
| • Mental ability tested with the Cattell Infant Intelligence scale | |||
| Nicovani (2009), Chile (27) | Kidney: 3 infants (triplet) | 4 years follow-up | • No specific long term outcome measures described |
| Xia (2008), China (17) | Liver: 1 infant | Follow-up 4 years, every 3–6 months | • Routine follow-up visits, patient self-examination of the baby’s growth and development |
| Scott (2002), United States (28) | Kidney: 5 infants (3 girls) (1 mother) | Follow-up at one time-point, age of the offspring: 23, 21, 18, 17, 15 years | • No outcome measurements described |
| Morini (1998), Italy (20) | Heart: 1 infant | Follow-up 14 months | • No specific long-term outcome measurements |
| Roll (1997), Germany (36) | Liver: 1 infant | Follow-up of 2 years and 6 months | • No specific long-term outcome measurements |
| Eskandar (1996), Canada (21) | Heart: 2 infants | Follow-up of >2 years in both children | • No specific long-term outcome measurements |
| Morita (1996), Japan (37) | Kidney: 8 infants | Mean follow-up: 4.1 years (range: 1 year till 11 years) | • 1-time point of evaluation. No specific method of assessment mentioned |
| Liljestrand (1993), Sweden (64) | Heart: 1 infant | Follow-up 18 months | • Specific long-term outcome measurements not described |
| • At 12 months: detailed evaluation at a regional specialized center in pediatric cardiology | |||
| Baarsma (1992), Netherlands (46) | Liver: 1 infant | Follow-up 2-year, not clear how many follow-up moments | • Immunological assessment of blood samples and functional assessment of the immune system |
| Grow (1991), United States (54) | Liver: 2 infants (twins) | Neurodevelopmental follow-up of 25 months | • Unspecified neurodevelopmental follow-up |
| Scantlebury (1990), United States (53) | Liver: 20 infants (1 twin) | Follow-up ranging from 9 months till 12 years (n = 16 > 1 year) | • No specific long-term outcome measurements described |
| Key (1989), United States (22) | Heart: 1 infant | Follow-up of 3 years | • No specific long-term outcome measurements described |
| Preieto (1989), Spain (23) | Kidney: 4 infants (2 sets of twins) | 1 twin follow-up at 22 months and 1 twin at 8 months | • No specific long-term outcome measurements described |
| Boner (1981), Israel (24) | Kidney: 2 infants (twins) | Follow-up of 6 years | • No specific long-term outcome measurements for the physical and psychological assessment described |
| • Cell mediated immunity examination at 8–10 months with blood samples: lymphocytic transformation measurement with phytohemaglutinin, estimation of the secretion of macrophage migration inhibition factor, PPD skin test, delayed hypersensitivity skin tests | |||
| Berant (1976), Israel (38) | Kidney: 1 infant | Multiple follow-up visits: at birth, 3 months, 5 months and 2 years | • Immunological evaluation with blood samples |
| • At birth: chest x-ray for the thymic shadow | |||
| • Lymphocytic transformation by phytohemagglutinin at birth and 2 years | |||
| Price (1976), United Kingdom (39) | Kidney: 2 infants | 1 child follow-up of 32 months and 1 child follow-up of 24 months. Not specified how many follow up moments | • No specific long-term outcome measurements described, developmental tests not specified |
| Control: 54 infants | • Blood lymphocyte, cortisol levels, and chromosome analyses measured at multiple timepoints |
Included studies, case reports.
Characteristics of Included Patients
A total of 1,664 live births were recorded, of which 78% (n = 1,290) were born after KTx, 17% (n = 287) after LiTx, 2.6% (n = 43) after HTx, 1.4% (n = 23) after combined pancreas-kidney transplantation, 1.1% (n = 18) after LuTx, and 0.2% (n = 3) after combined heart-lung transplantation. In pregnancies of which the complete immunosuppressive regimen was known, 78% of the women used corticosteroids, 49% cyclosporine, 41% azathioprine, and 30% tacrolimus. In 51 pregnancies with a live birth mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) was used for at least part of gestation, in five pregnancies rapamycin, and in one pregnancy everolimus. Two studies did not specify if MMF and/or rapamycin was stopped during pregnancy (12, 13). No congenital abnormalities were mentioned in these live-born children. Details on gestational age and birth weight can be found in Supplementary Tables S2A,S2B. In 15 articles (n = 191 children, 12%) “normal development,” “no problems,” or “doing well” was mentioned without conducting specific tests or parameters (14–28).
Growth
Specific results on growth were described in 16 articles (11, 29–43), of which 6 are case reports (29, 36–39, 41). Overall these results indicate that growth development in the offspring of SOT patients is normal. Of the 234 children born after KTx, 219 (94%) had weight and length development comparable to the general population (11, 30–33, 37–40, 42, 43). Sgro et al. reported a significantly higher weight for age and a significantly lower length for age at a mean follow-up of 3.1 years (range 3 months-11 years) in the KTx offspring group compared to the control group (31). Schreiber-Zamora et al. reported no significant differences in the prevalence of overweight and underweight when comparing offspring of KTx recipients (KTR) with offspring of LiTx recipients and a control group. In the transplant group 16.4% had obesity and in the control group 6.3% did (p = 0.072). The theoretical incidence of obesity in the general population (5%) was significantly lower than the incidence in the LiTx (17.1%), the KTx offspring (15.4%), and the overall transplant group (16.4%) (p < 0.001, p = 0.02, p < 0.001 respectively). Prenatal exposure to tacrolimus was associated with a 2.8-fold increased risk for developing a higher body mass index at later follow-up (42).
Catch-up growth was reported in three case reports with three children from KTR and one child from a LiTx recipient (36, 38, 39). Willis et al. also reported impressive catch-up growth in 21 children born with a birth weight <10th percentile (33). In five articles the growth of 86 infants born after LiTx was evaluated; even though birth weight was low, subsequent height and weight development was within the normal range (29, 34–36, 42).
Immunological Follow-Up
Ten studies focused on immunological follow-up of the offspring (18, 29, 38, 39, 44–49), of which four were case reports (29, 38, 39, 46). In none of the included studies were opportunistic or chronic infections reported. Antibody response to vaccination was normal and no side-effects of vaccination were observed (18, 38, 45, 46). Two studies reported a significantly higher number of children hospitalized due to infectious disease in the KTx offspring group compared to a control group (44, 49). Ono et al. reported that 28.6% of the KTx group compared to 7.5% of the unmatched control group was hospitalized (p = 0.046) (44). All hospitalized children were exposed to tacrolimus during pregnancy. Egerup et al. matched a KTx offspring group aged 0–5 years with a control group in a 1:10 ratio. 41.9% of the KTx offspring compared to 24.8% of the control group were hospitalized due to infectious disease (risk ratio 1.67). The average number of antibiotic prescriptions filled between age 1–5 years was significantly higher in the KTx compared to the controls. However, this difference was not observed in the group as a whole (age 0–5 years) and not for group <1 year (Supplementray Table S2A) (49).
Serum levels of IgA, IgM, and IgG within the normal range were reported (29, 38, 47, 48). Moreover, Drozdowska et al. found no differences in IgG and IgM concentrations between 39 children of KTR and 39 age-matched controls (age one day-15 years) (48). At birth low numbers of total lymphocytes and specific lymphocyte subsets were reported in three studies, but in 28 of these 31 children normal lymphocyte counts were found at a maximum follow-up of 2 years (39, 44, 46). Ono et al. reported a significantly lower percentage of transitional B cells (CD19+CD10+) and a higher expression of CD154 on CD4+ T cells in children exposed to tacrolimus compared to children exposed to cyclosporine (p = 0.029 and p = 0.009 respectively) (44). Pilarski et al. reported that in an offspring group (n = 10, range 5 months-9 years) compared to a control group, cyclosporine-exposed children had significantly higher numbers of CD45RA + R0- T cells and azathioprine-exposed children had significantly higher numbers of CD45RA-R0+ T cells, suggesting that cyclosporine exposure delayed T cell development and azathioprine exposure accelerated T cell development (45). Moreover, children exposed to cyclosporine had a lower and to azathioprine a higher expression of CD29 T cells compared to the control group (45).
In summary, normal response to vaccination and no opportunistic infection were reported but, especially at young age, the results show some alterations in numbers of immune cells in the transplant offspring group and two studies indicate an increased risk of hospitalization for infection.
Neurobehavioral and Cognitive Follow-Up
Sixteen articles conducted specific tests on neurobehavioral development or cognition (11, 13, 29–31, 33, 37, 45, 47, 50–56), of which three are case reports (29, 53, 54). The studies show that neurological development is similar to the general population. Five articles described intelligence quotient (IQ) scores (11, 29, 30, 50, 52). No significant differences regarding global intellectual performance were found when comparing the transplant offspring with the general population or matched control groups at infant, toddler, pre-school, and school age (11, 30, 50). However, Morales-Buenrostro et al. reported that visuospatial working memory might be affected in preschool children born after KTx (p = 0.007) (50). No significant differences in IQ scores were found between children only exposed to cyclosporine and children exposed to both cyclosporine and azathioprine (30). Subgroup analyses with mothers taking MMF prior to their awareness of being pregnant did not show statistical differences in full scale IQ (50). Kocisezwska-Najman et al. found no differences in the distribution of IQ between children born to LiTx and KTx recipients, though children of KTR had significantly higher percentages of preterm birth and LBW (risk factors for lower IQ) (57) compared to offspring of LiTx recipients (52). Devresse et al. reported that 8/21 (38%) children had a grade repetition, which is lower than their country’s general population (60%) (13).
In 296 children neurodevelopmental follow-up was performed without comparison to a control group (31, 33, 37, 47, 53–55). In 87% no developmental problems were reported and in 13% developmental delays, such as the need for educational support or neurological abnormalities such as cerebral palsy, slightly delayed psychomotor development, and intellectual disability, were reported.
Kidney Function
Eight studies mentioned specific results on kidney function (12, 13, 26, 32, 33, 58–60). No abnormalities in kidney function were reported in 96% (243/252) of the assessed children. Al-Khader et al. reported no signs of glomerular or tubular defects and no hypertension or proteinuria in 41 children born from KTR at a mean follow-up of 52 months (12). In 95% of these pregnancies a calcineurin inhibitor (CNI, 73% cyclosporine, 22% tacrolimus) was used. Giudice et al. also reported no renal abnormalities in 12 children born from KTR at a mean follow-up of 2.6 years (32). In all these pregnancies cyclosporine was used during pregnancy. Willis et al. reported 4/40 (10%) children with urinary tract abnormalities on ultrasound: one ureteropelvic junction obstruction, one unilateral scar, and two unilateral renal dysplasia (two female siblings). These two female siblings also had abnormalities on urine analyses. 50% of the mothers used cyclosporine during pregnancy. The reported 10% is significantly more than the general population (2.9%, p = 0.036) (33). Dębska-Slizien et al. reported one child with symptoms of glomerulonephritis out of 22 children born to KTR (26). Borek-Dziecioł et al assessed kidney function parameters (urea, creatinine, potassium, and sodium concentrations) in 40 infants (newborns and children aged >1 year, age not specified) born to mothers with a KTx and 40 control infants matched to gestational age. They did not find any significant differences between the KTx and the control group, nor did they find any differences between the immunosuppressive regimens use by the mothers (58). Shaheen et al. analyzed basic kidney function parameters in the blood of offspring born to KTR as well (median age 39 months, range 6–72 months) and did not find problems in renal functioning or integrity (59). Devresse et al. analyzed questionnaires of 21 children born after KTx aged 7–25 years. None of the children reported taking any chronic medication and no one reported a history of chronic kidney disease, renal stones, gross hematuria, or pathological urine dipstick at school medicine (13). Czaplinska et al. assessed liver function (AST, ALT) and kidney function (creatinine and urea) in 51 infants born to mothers with a LiTx (newborns and children aged >1 year, age not specified). They did not find significant differences between the LiTx group and the control group matched to gestational age and time period of birth, except for significantly lower ALT levels in the LiTx group (60).
Other Findings
One study with a relatively large sample size (n = 199 live births) reported significantly more cases of acute bronchitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and hyperactivity disorders in the KTx offspring compared to the matched control group (p = 0.007, p = 0.025, p = 0.038 resp.) (61). The same study reported a significantly higher number of hospitalizations in the transplant offspring group compared to the control group (65.8% vs. 45.6%, p < 0.001), without specifying the reason for admission (61). One study focused on ophthalmological follow-up in children aged 1 week till >6 years (not further specified); no differences in pathological findings between the offspring of LiTx, KTx and the control group were found (62).
Bar et al. reported no significant difference in the rate of severe disability in the long-term; there were 8% (n = 3) in the transplant offspring group (two cases of cerebral palsy due to extreme prematurity and one deaf child, probably due to a cytomegalovirus infection) and 2.4% (n = 1) in the primary renal disease group (63). In one case report and one retrospective cohort study, two cases of hepatoblastoma at young age (2.5 years and 18 months) were reported: one child of a LiTx recipient and one child of a KTR (36, 43). One child born to a mother with a HTx had a serious, probably hereditary, cardiac insufficiency (64).
Fathers With a History of a Transplantation
One article (11), described longer term follow-up of children born to fathers with a history of a SOT (11). Four children born to three fathers with a KTx were described. At follow-up (age 4 months, 10 months, 11 months and 2 years 7 months) no abnormalities were found on physical examination except for one child with sickle cell trait. The height percentiles were 25th, 25th, 55th, and 75th percentile and the weight percentiles were 10th, 45th, 75th, and 95th. On the Bayley Scales Mental Development Index the offspring scored within the range of normal (82, 83, 105, and 120).
Discussion
To the best of our knowledge this is the first systematic review evaluating the available data regarding longer term (>1 year) outcomes of children of SOT patients. In general, we found that pregnancy after SOT appears to have reassuring longer term outcomes. Most children had normal physical and neurobehavioral development, despite frequent preterm birth and/or LBW.
The included studies reported high percentages of preterm birth and LBW in infants of mothers with a SOT. Precise numbers of preterm birth and LBW could not be calculated since some of the articles only mentioned mean or median gestational age and birth weight without giving the number of children fulfilling the definitions. In general, women who get pregnant after SOT are a selected population of patients who do well after transplantation. In this selected population, in line with our results on perinatal outcomes, previous research reported high preterm birth rates of 32% after LiTx (65) and 43% after KTx (3). Preterm birth and LBW are associated with poor growth in the first 2 years of life, as well as lower motor and cognitive scores compared to term infants (57). Interestingly, this is not in line with the data on offspring of mothers with SOT presented in this systematic review. Length and weight development was within the normal range in almost all children, including in children that were born preterm and/or with LBW, suggesting that the effects of transplantation and immunosuppressive medication on these outcomes are transient. A possible explanation for this difference is that the underlying mechanism leading to preterm birth and LBW is different in SOT recipients compared to the general population. Placentation is affected by the history of a SOT and especially by KTx, and the vascular remodeling in pregnancy is likely to be affected by immunosuppressive medication (66). Of the immunosuppressive medication, fetal exposure to CNIs especially is concerning, since approximately 70% of maternal tacrolimus and 37%–64% of maternal cyclosporine concentrations reach the fetus. Corticosteroids freely cross the placenta but 90% is metabolized to inactive forms in the placenta and azathioprine cannot be converted to its active form in the human fetal liver (6). However, the rate of obstetric complications such as preterm birth and LBW is similar in post-transplantation pregnancies on different immunosuppressive regimens, suggesting that immunosuppressive medication is not the only factor affecting the risk of complications (6).
The included studies show that results of neurological and cognitive assessment are similar to the general population. The results of our systematic review are in line with the TPRI that also suggests that cognitive and physical development of the children (>1,500 children) is comparable to the general population although their data is subject to reporting bias because of collection via voluntary patient questionnaires (1).
On immunological follow-up some abnormalities were seen. Low numbers of lymphocytes shortly after birth are reported in studies included in this review (39, 44, 46) and in other studies with a follow-up of <1 year (67, 68). However, lymphocyte numbers normalized at longer follow-up. Some differences in levels of subtypes of immune cells between immunosuppressive medications were observed. The relevance of these findings is arguable since no differences in immunological complications between the different immunosuppressive regimens were reported. Moreover, in none of the 1,664 children were opportunistic or chronic infections reported. Three studies reported a significantly higher number of hospitalizations in children born to transplanted mothers, including a higher number of antibiotic prescriptions in one study (44, 49, 61). A possible explanation for the increased rate of hospitalization in the transplant offspring is increased alertness to possible problems by their mothers and/or doctors. It is likely that the upbringing of children is influenced by the SOT of the mother. For example, maternal anxiety about her own and the child’s health may lead to increased care seeking behavior (11). Besides, some of the complications such as the reported kidney abnormalities may be due to hereditary risk and are not necessarily linked to the transplantation itself.
Several limitations of this systematic review must be acknowledged. A main limitation is the large proportion of case reports and retrospective studies that may be subjected to publication bias. However, of the included studies 16/53 had a control group (58% of the offspring, n = 960). Furthermore, most data presented here focused on childhood outcomes. Only five studies included offspring aged >18 years in their study group. Another limitation is that the majority of births (78%) presented here are after KTx. Therefore, it is difficult to draw conclusions about differences between the types of SOT. Future research should focus on the long-term follow-up of offspring born after SOT at multiple time points and preferably into adult age, since it could be hypothesized that in utero exposure to immunosuppressive medication could lead to vascular damage which in turn leads to organ damage later in life. It seems plausible that immunosuppressive medication, which has nephrotoxic side-effects in the transplant population, affects the development of the kidneys in the offspring. Fortunately, the existing studies described here are reassuring. However, the majority of the offspring were evaluated at a relatively young age. It would be possible that there are already small (non-significant) health problems in these children that become apparent at an older age. Future research should assess if problems at later age arise. This would be in line with findings in antenatal exposure to cyclosporine in rabbits whereby nephrological abnormalities and systemic hypertension occur, worsening with advanced age (69).
In conclusion, this systematic review shows that the majority of offspring of SOT patients are healthy and develop well. These findings are encouraging for patients considering pregnancy after SOT and should be discussed in preconception counseling. However, this systematic review also shows that existing information is scarce and predominantly limited to small studies with young children. Larger and longer prospective studies with long-term follow-up into adulthood of these children are necessary to optimize pregnancy counselling of SOT patients.
Statements
Author contributions
JM: Study design, data collection, data analysis, bias appraisal and manuscript writing. JP: Bias appraisal, manuscript writing and critical review. SB: Manuscript writing and critical review. MJ: Study design, data collection, data analysis and manuscript writing.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontierspartnerships.org/articles/10.3389/ti.2022.10565/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
HTx, heart transplantation; IQ, intelligence quotient; JBI, Joanna Briggs Institute; KTR, kidney transplant recipient; KTx, kidney transplantation; LBW, low birth weight; LiTx, liver transplantation; LuTx, lung transplantation; MMF, mycophenolate mofetil; NOS, Newcastle Ottawa Scale; PRISMA, preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analyses; SOT, solid organ transplantation.
References
1.
Constantinescu MJMS. Transplant Pregnancy Registry International, 2019 Annual Report. Philadelphia, PA: Transplant Pregnancy Registry International TPRI (2020). Google Scholar
2.
Durst JK Rampersad RM . Pregnancy in Women with Solid-Organ Transplants: a Review. Obstet Gynecol Surv (2015) 70:408–18. 10.1097/OGX.0000000000000194PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
3.
Shah S Venkatesan RL Gupta A Sanghavi MK Welge J Johansen R et al Pregnancy Outcomes in Women with Kidney Transplant: Metaanalysis and Systematic Review. BMC Nephrol (2019) 20:24. 10.1186/s12882-019-1213-5PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
4.
Deshpande NA James NT Kucirka LM Boyarsky BJ Garonzik-Wang JM Cameron AM et al Pregnancy Outcomes of Liver Transplant Recipients: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Liver Transpl (2012) 18:621–9. 10.1002/lt.23416PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
5.
Piccoli GB Cabiddu G Attini R Gerbino M Todeschini P Perrino ML et al Pregnancy Outcomes after Kidney Graft in Italy: Are the Changes over Time the Result of Different Therapies or of Different Policies? A Nationwide Survey (1978-2013). Nephrol Dial Transpl (2016) 31:1957–65. 10.1093/ndt/gfw232CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
6.
Klein CL Josephson MA . Post-transplant Pregnancy and Contraception. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol (2022) 17:114–20. 10.2215/CJN.14100820PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
7.
Moher D Liberati A Tetzlaff J Altman DG . Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: the PRISMA Statement. Ann Intern Med (2009) 151:264–9. 10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
8.
Wells GA Shea B O'Connell D Peterson J Welch V Losos M et al The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses (2013). Available at: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp.
9.
Moola SMZ Tufanaru C Aromataris E Sears K Sfetcu R Currie M et al Chapter 7: Systematic Reviews of Etiology and Risk. In: Aromataris EMZ, editor. JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis JBI (2020). CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
10.
Wilmott RW . “Catching-up” on Catch-Up Growth. J Pediatr (2013) 162:220. 10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.12.021CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
11.
Korsch BM Klein JD Negrete VF Henderson DJ Fine RN . Physical and Psychological Follow-Up on Offspring of Renal Allograft Recipients. Pediatrics (1980) 65:275–83. 10.1542/peds.65.2.275PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
12.
Al-Khader A Basri N Qureshi J Shaheen Hejaili Flaiw et al Pregnancies in Renal Transplant Recipients-Wwith a Focus on Babies. Ann Transpl (2004) 9:65–7. Google Scholar
13.
Devresse A Jassogne C Hubinont C Debieve F De Meyer M Mourad M et al Pregnancy Outcomes after Kidney Transplantation and Long-Term Evolution of Children: A Single Center Experience. Transpl Proc (2022) 54:652–7. 10.1016/j.transproceed.2022.01.019CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
14.
Turkyilmaz G Yasa C Dural O Erturk E Kalelioglu I Has R et al Pregnancy in Liver Transplant Recipients: A Single center Outcomes. J Obstet Gynaecol Res (2018) 44:1882–6. 10.1111/jog.13718PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
15.
Mahmoud T Mujaibel K Attia H Zakaria Z Yagan J Gheith O et al Triplet Pregnancy in a Diabetic Mother with Kidney Transplant: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Exp Clin Transpl (2017) 15:139–46. 10.6002/ect.mesot2016.P23CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
16.
Shaner J Coscia LA Constantinescu S McGrory CH Doria C Moritz MJ et al Pregnancy after Lung Transplant. Prog Transpl (2012) 22:134–40. 10.7182/pit2012285CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
17.
Xia D He H-Y Xu L Quan Y Zuo HQ Yan LN et al Pregnancy after Liver Transplantation: Four-Year Follow-Up of the First Case in mainland China. World J Gastroenterol (2008) 14:7264–6. 10.3748/wjg.14.7264PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
18.
Miniero R Tardivo I Curtoni ES Bresadola F Calconi G Cavallari A et al Outcome of Pregnancy after Organ Transplantation: a Retrospective Survey in Italy. Transpl Int (2004) 17:724–9. 10.1007/s00147-004-0781-9PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
19.
McGrory CH Radomski JS Moritz MJ Armenti VT . Pregnancy Outcomes in 10 Female Pancreas-Kidney Recipients. J Transpl Coord (1998) 8:55–9. 10.7182/prtr.1.8.1.w3128326211737k1PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
20.
Morini A Spina V Aleandri V Cantonetti G Lambiasi A Papalia U . Pregnancy after Heart Transplant: Update and Case Report. Hum Reprod (1998) 13:749–57. 10.1093/humrep/13.3.749PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
21.
Eskandar M Gader S Ong BY . Two Successful Vaginal Deliveries in a Heart Transplant Recipient. Obstet Gynecol (1996) 87:880. PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
22.
Key TC Resnik R Dittrich HC Reisner LS . Successful Pregnancy after Cardiac Transplantation. Am J Obstet Gynecol (1989) 160:367–71. 10.1016/0002-9378(89)90447-xPubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
23.
Preieto C Errasti P Olaizola J Morales JM Andres A Medina C et al Successful Twin Pregnancies in Renal Transplant Recipients Taking Cyclosporine. Transplantation (1989) 48:1065–7. 10.1097/00007890-198912000-00035PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
24.
Boner G Bott‐Kanner G Schweitzer A Danon YL Rosenfeld JB . Successful Multiple Pregnancy in Renal Transplant Recipient. Int J Gynaecol Obstet (1981) 19:251–4. 10.1016/0020-7292(81)90070-9PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
25.
Wagoner LE Taylor DO Olsen SL Price GD Rasmussen LG Larsen CB et al Immunosuppressive Therapy, Management, and Outcome of Heart Transplant Recipients during Pregnancy. J Heart Lung Transpl (1993) 12:993. Google Scholar
26.
Dębska-Ślizień A Gałgowska J Bułło-Piontecka B Bzoma B Chamienia A Krol E et al Pregnancy after Kidney Transplantation with Maternal and Pediatric Outcomes: A Single-Center Experience. Transpl Proc (2020) 52:2430–5. 10.1016/j.transproceed.2020.01.122CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
27.
Nicovani V Poblete H Toro J Carrera M Pérez L . Successful Multiple Pregnancy (Triplets) in a Kidney Transplant Recipient: a Case Report. Transpl Proc (2009) 41:2688–90. 10.1016/j.transproceed.2009.06.129CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
28.
Scott JR Branch DW Holman J . Autoimmune and Pregnancy Complications in the Daughter of a Kidney Transplant Patient. Transplantation (2002) 73:815–6. 10.1097/00007890-200203150-00028PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
29.
Kociszewska-Najman B Pietrzak B Jabiry-Zieniewicz Z Mazanowska N Wielgoś M . Pregnancy after Living Related Liver Transplantation-Aa Report of Two Cases. Ann Transpl (2012) 17:120–5. 10.12659/aot.883466CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
30.
Nulman I Sgro M Barrera M Chitayat D Cairney J Koren G et al Long-term Neurodevelopment of Children Exposed In Utero to Ciclosporin after Maternal Renal Transplant. Paediatr Drugs (2010) 12:113–22. 10.2165/11316280-000000000-00000PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
31.
Sgro MD Barozzino T Mirghani HM Sermer M Moscato L Akoury H et al Pregnancy Outcome post Renal Transplantation. Teratology (2002) 65:5–9. 10.1002/tera.1092PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
32.
Giudice PL Dubourg L HAdj-AissA A Claris O Audra P . Renal Function of Children Exposed to Cyclosporin In Utero. Nephrol Dial Transpl (2000) 15:1575–9. 10.1093/ndt/15.10.1575CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
33.
Willis F Findlay C Gorrie M Watson M Wilkinson A Beattie T et al Children of Renal Transplant Recipient Mothers. J Paediatr Child Health (2000) 36:230–5. 10.1046/j.1440-1754.2000.00500.xPubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
34.
Wu A Nashan B Messner U NieSert S Guenther HH . Outcome of 22 Successful Pregnancies after Liver Transplantation. Clin Transpl (1998) 12:454–64. Google Scholar
35.
Jain A Venkataramanan R Fung JJ Lever J Balan V . Pregnancy after Liver Transplantation under Tacrolimus. Transplantation (1997) 64:559–65. 10.1097/00007890-199708270-00002PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
36.
Roll C Luboldt H-J Winter A Voit T Erhard J . Hepatoblastoma in a 2-Year-Old Child of a Liver-Transplanted Mother. Lancet (1997) 349:103. 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)60887-2CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
37.
Morita K Seki T Shinojima H TabaTa T Chikaraishi T Tanda K et al Parturition in Six Renal Allograft Recipients. Int J Urol (1996) 3:54–7. 10.1111/j.1442-2042.1996.tb00630.xPubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
38.
Berant M Wagner Y Jacob ET Levin S Handzel ZT . Immunologic Status of the Offspring of A Cadaver Kidney Recipient: Normal Findings in a Long-Term Follow-Up Study. Clin Pediatr (1976) 15:815–8. 10.1177/000992287601500911CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
39.
Price H Salaman J Laurence K Langmaid H . Immunosuppressive Drugs and the Foetus. Transplantation (1976) 21:294–8. 10.1097/00007890-197604000-00004PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
40.
Bachmann F Budde K Gerland M Wiechers C Heyne N Nadalin S et al Pregnancy Following Kidney Transplantation - Impact on Mother and Graft Function and Focus on Childrens' Longitudinal Development. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth (2019) 19:376. 10.1186/s12884-019-2496-zPubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
41.
Rao NN Wilkinson C Morton M Bennett GD Russ GR Coates PT et al Successful Pregnancy in a Recipient of an ABO-Incompatible Renal Allograft. Obstet Med (2019) 12:42–4. 10.1177/1753495X17745390PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
42.
Schreiber-Zamora J Szpotanska-Sikorska M Czaplinska N Drozdowska-Szymczak A Pietrzak B Wielgos M et al Evaluation of the Body Mass index (BMI) in Children Born to Organ Transplant Recipients. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med (2019) 32:2512–6. 10.1080/14767058.2018.1439468PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
43.
Pahl MV Vaziri ND Kaufman DJ Martin DC . Childbirth after Renal Transplantation. Transpl Proc (1993) 25:2727–31. Google Scholar
44.
Ono E Dos Santos A Viana P Dinelli MIS Sass N De OLiveira L et al Immunophenotypic Profile and Increased Risk of Hospital Admission for Infection in Infants Born to Female Kidney Transplant Recipients. Am J Transpl (2015) 15:1654–65. 10.1111/ajt.13143CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
45.
Pilarski LM Yacyshyn BR Lazarovits AI . Analysis of Peripheral Blood Lymphocyte Populations and Immune Function from Children Exposed to Cyclosporine or to Azathioprine In Utero. Transplantation (1994) 57:133–44. 10.1097/00007890-199401000-00021PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
46.
Baarsma R Kamps W . Immunological Responses in an Infant after Cyclosporine A Exposure during Pregnancy. Eur J Pediatr (1993) 152:476–7. 10.1007/BF01955053PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
47.
Rasmussen P Fasth A Ahlmen J Brynger H Iwarson S Kjellmer I . Children of Female Renal Transplant Recipients. Acta Paediatr Scand (1981) 70:869–75. 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1981.tb06242.xPubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
48.
Drozdowska-Szymczak A Kociszewska-Najman B Schreiber-Zamora J Borek-Dzieciol B Zwierzchowsk A . Evaluation of Selected Markers of the Immune System in Children of Renal Transplant Recipients. Transpl Proc (2014) 46:2703–7. 10.1016/j.transproceed.2014.09.062CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
49.
Egerup P Carlson N Bruun Oestergaard L Blanche P Scott JR Hornum M et al Increased Risk of Neonatal Complications and Infections in Children of Kidney-Transplanted Women: A Nationwide Controlled Cohort Study. Am J Transpl (2021) 21:1171–8. 10.1111/ajt.16259CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
50.
Morales-Buenrostro LE Alberu J Mancilla-Urrea E Velez-Garcia A Espinoza-Perez R Cruz-Santiago J et al Intellectual Performance of Kidney Transplant Recipients’ Offspring: a Cross-Sectional, Multicenter Study. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med (2019) 32:542–9. 10.1080/14767058.2017.1384805PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
51.
Schreiber-Zamora J Szpotanska-Sikorska M Drozdowska-Szymczak A Czaplinska N Pietrzak B Wielgos M et al Neurological Development of Children Born to Mothers after Kidney Transplantation. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med (2019) 32:1523–7. 10.1080/14767058.2017.1407754PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
52.
Kociszewska-Najman B Szpotanska-Sikorska M Mazanowska N Wielgos M Pietrzak B . The Comparison of Intelligence Levels of Children Born to Kidney or Liver Transplant Women with Children of Healthy Mothers. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med (2018) 31:3160–5. 10.1080/14767058.2017.1365131PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
53.
Scantlebury V Gordon R Tzakis A Bowman J Mazzaferro V . Childbearing after Liver Transplantation. Transplantation (1990) 49:317–21. 10.1097/00007890-199002000-00018PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
54.
Grow DR Simon NV Liss J Delp WT . Twin Pregnancy after Orthotopic Liver Transplantation, with Exacerbation of Chronic Graft Rejection. Am J Perinatol (1991) 8:135–8. 10.1055/s-2007-999362PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
55.
Wong K Bailey R Lynn K Robson R Abbott G . Pregnancy in Renal Transplant Recipients: the Christchurch Experience. N Z Med J (1995) 108:190–2. PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
56.
Stanley CW Gottlieb R Zager R Eisenberg J Richmond R Moritz MJ et al Developmental Well-Being in Offspring of Women Receiving Cyclosporine post-renal Transplant. Transpl Proc (1999) 31:241–2. 10.1016/s0041-1345(98)01519-xCrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
57.
Scharf RJ Stroustrup A Conaway MR DeBoer MD . Growth and Development in Children Born Very Low Birthweight. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed (2016) 101:F433–8. 10.1136/archdischild-2015-309427PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
58.
Borek-Dziecioł B Czaplinska N Szpotanska-Sikorska M Mazanowska N Schreiber-Zamora J Jabiry-Zieniewicz Z et al Selected Biochemical Parameters in Children of Mothers after Kidney Transplantation. Transpl Proc (2020) 52:2294–8. 10.1016/j.transproceed.2020.02.100CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
59.
Shaheen FA al-Sulaiman MH al-Khader AA . Long-term Nephrotoxicity after Exposure to Cyclosporine In Utero. Transplantation (1993) 56:224–5. 10.1097/00007890-199307000-00044PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
60.
Czaplińska N Kociszewska-Najman B Schreiber-Zamora J Wilkos E DrozdowskA-SzymczAk A Borek-Dzieciol B et al Analysis of the Selected Biochemical Parameters of Liver and Kidney Function in Children of Mothers after Liver Transplantation. Transpl Proc (2014) 46:2790–3. 10.1016/j.transproceed.2014.09.059CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
61.
Norrman E Bergh C Wennerholm U-B . Pregnancy Outcome and Long-Term Follow-Up after In Vitro Fertilization in Women with Renal Transplantation. Hum Reprod (2014) 30:205–13. 10.1093/humrep/deu293PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
62.
Kociszewska-Najman B Pietrzak B Moneta-Wielgos J Samaha R Wielgos M . Study of the Ophthalmic System of Babies Delivered to Transplant Recipients. Transplantation (2013) 95:847–51. 10.1097/TP.0b013e31827f84dbPubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
63.
Bar J Stahl B Hod M Wittenberg C Pardo J Merlob P . Is Immunosuppression Therapy in Renal Allograft Recipients Teratogenic? A Single-center Experience. Am J Med Genet A (2003) 116:31–6. 10.1002/ajmg.a.10817CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
64.
Liljestrand J Lindström B . Childbirth after post Partum Cardiac Insufficiency Treated with Cardiac Transplant. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand (1993) 72:406–8. 10.3109/00016349309021124PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
65.
Prodromidou A Kostakis ID Machairas N StamoPoulos P PAspAlA A . Pregnancy Outcomes after Liver Transplantation: A Systematic Review. Transpl Proc (2019) 51:446–9. 10.1016/j.transproceed.2019.01.014CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
66.
Brosens I Brosens JJ Benagiano G . The Risk of Obstetrical Syndromes after Solid Organ Transplantation. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol (2014) 28:1211–21. 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2014.08.001PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
67.
Dinelli MIS Ono E Viana PO Spina FG Weckx LY Dos Santos AMN et al Response to Immunization in Children Born to Renal Transplant Recipients Using Immunosuppressive Drugs during Gestation. Vaccine (2016) 34:404–7. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.12.017PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
68.
Schena F Stallone G Schena A Derosa C Procino A . Pregnancy in Renal Transplantation: Immunologic Evaluation of Neonates from Mothers with Transplanted Kidney. Transpl Immunol (2002) 9:161–4. 10.1016/s0966-3274(02)00028-xPubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
69.
Tendron-Franzin A Gouyon JB Guignard JP Decramer S Justrabo E Gilbert T et al Long-term Effects of In Utero Exposure to Cyclosporin A on Renal Function in the Rabbit. J Am Soc Nephrol (2004) 15:2687–93. 10.1097/01.ASN.0000139069.59466.D8PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Summary
Keywords
transplantation, long-term, offspring, follow-up, pregnancy
Citation
Meinderts JR, Prins JR, Berger SP and De Jong MFC (2022) Follow-Up of Offspring Born to Parents With a Solid Organ Transplantation: A Systematic Review. Transpl Int 35:10565. doi: 10.3389/ti.2022.10565
Received
12 April 2022
Accepted
06 July 2022
Published
05 August 2022
Volume
35 - 2022
Updates
Copyright
© 2022 Meinderts, Prins, Berger and De Jong.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Margriet F. C. De Jong, m.f.c.de.jong@umcg.nl
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.