Abstract
Coxsackieviruses (CVs) belong to the genus Enterovirus and family Picornaviridae. Mutants can arise within the replication cycle of RNA viruses. The prototype CVB2 Ohio-1 (CVB2/O) strain adapted to rhabdomyosarcoma (RD) cells induced cytolytic infection and showed three-point mutations in the genome (CVB2/O/RD). The aim of this experimental study was to compare the effect of one or multiple viral mutations in viral protein 1 (VP1) or region 2C of CVB2/O on pathogenesis in two different mouse models. Male A/J and CD1 (10–12 g) mice were infected intraperitoneally with CVB2/O and its mutants or mock infected (control mice). Mice were sacrificed on days 0, 5, 7, 10, and 55 post infection. Blood, heart, and pancreas were collected for virological and histopathological analysis. The presence of viral RNA in the heart and pancreas of infected mice was studied. Different cytokines were detected in the serum. Pathological changes were absent in the hearts of infected mice. Maximum pathological changes were identified in the pancreas of infected A/J mice. Infiltration of pancreatic cells was observed depending on the mouse strain and mutants. CD1 mice were less susceptible to CVB2 infection. CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K mutant induced maximum changes in the pancreas of A/J-infected mice. We suggest that the single altered amino acid in the VP1 protein was related to the virulence factor and was associated with the pathology and presence of viral RNA in the pancreas of infected A/J mice.
Introduction
Mutations arise spontaneously in the genome because of the adaptation process to complex environments and allow virus survival, a phenomenon common in RNA viruses. The genetic flexibility and constant variation of enteroviruses (EVs) make them potential agent of emerging infectious diseases, and there is a need to develop new anti-EV compounds and vaccinations (Domingo et al., 2008). Mutations can affect virus-cell interactions, thus tissue tropism, and can ultimately alter the pathogenesis of viral infection. Although EVs are predominantly cytolytic, they can also cause persistent infections (Argo et al., 1992; Frisk et al., 1999; Schmidtke et al., 2000). In the process of adaptation, picornaviruses have the potential to accommodate to a new host system, with various genomic mutations occurring during the life cycle that can trigger cell apoptosis (Lukashev, 2005).
Coxsackieviruses (CVs) are ubiquitous, small, positive single-stranded RNA viruses belonging to the genus Enterovirus, species Enterovirus betacoxsackie (Enterovirus B), and the Picornaviridae family1. CVB2 is endemic, although occasional outbreaks of minor epidemics may occur (Polacek et al., 1999; Khetsuriani et al., 2006; Huang et al., 2015). Enterovirus variability in the environment is high, CVB2 mutants occur in the population and may cause severe disease in patients (Machado et al., 2024). CVB2 isolates have been established as etiological agents in neurological infections (aseptic meningitis and encephalitis), multiorgan failure and cardiogenic shock, hand, foot, and mouth disease, and myocarditis (Hong et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2017; Hopkins et al., 2019; Sousa et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2022; Kriger et al., 2023; Fratty et al., 2024). Hong et al. (2017) examined two CVB2 isolates from patients with different clinical symptoms (acute myocarditis and aseptic meningitis) and found high homology of the nucleotide sequences of the isolates with the prototypical CVB2/O strain. Polacek et al. (1999) determined the complete CVB2 sequence from the prototype strain. In the genome of the prototype CVB2 Ohio-1 (CVB2/O) strain adapted to human rhabdomyosarcoma (RD) cells (CVB2/O/RD) causing cytolytic infection, three mutations related to apoptotic activity were detected. Two amino acid substitutions were in the viral capsid protein (VP1) 1 region (I to F at position 118 and Q to K at position 164), the other in the 2C (K to R at position 185) coding region (Polacek et al., 2005). The single- or multiple-amino acid mutants were prepared by site-specific mutagenesis. The mutant CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K was found to have a distinct mutation that distinguished between persistent and cytolytic infection in RD cells. The triple mutant CVB2/O/RD caused pancreatitis in mice (Gullberg et al., 2010).
Our aim was to evaluate the impact of different variants of CVB2 (with single/double mutations) on pathogenesis in A/J and CD1 mouse models until day 55 p.i. and whether the single mutation on the VP1 protein of CVB2/O (amino acid substitution Q to K at position 164) correlates with pancreatitis in mice and immunological status.
Materials and methods
Cells and viruses
Green monkey kidney (GMK) and RD cells, were kindly provided by prof. Lindberg (Department of Chemistry and Biomedical Sciences, Faculty of Health and Life Sciences, Linnaeus University, Kalmar, Sweden). Human epithelial (HEp-2) cells were obtained from the Office of Public Health (Bratislava, Slovakia). All cells were maintained in Eagle´s minimum essential medium (EMEM) supplemented with 100 U/mL penicillin, 0.1 mg/mL streptomycin, 1% HEPES [4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid] and 5%–10% heat-inactivated bovine serum for cell growth and 2% for viral infection at 37°C.
Prototype CVB2/O strain and its variants: CVB2/O/RD-II/VP1 (double mutant, containing both I118F and Q164K substitutions in VP1 region), CVB2/O/VP1-I118F (single mutant in VP1 region), CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K (single mutant in VP1 region), and CVB2/O/2C-K185R (single mutant in 2C region) were provided by prof. Lindberg (Department of Chemistry and Biomedical Sciences, Faculty of Health and Life Sciences, Linnaeus University, Kalmar, Sweden). The viruses were propagated in GMK and RD cells and the virus titer was determined by the Spearman-Kärber method (Spearman, 1908; Kärber, 1931; Hierholzer and Killington, 1996).
Mice infection
Male inbred A/JOlaHsd (A/J, Harlan, United Kingdom) and outbred CD1 (Harlan Laboratories, Italy) mice, weighing 10–12 g, were housed in sterile pathogen-free conditions with access to sterile water and commercial food, in rooms controlled for temperature, 12/12 h light/dark cycle and humidity. After quarantine, both mice strains were infected intraperitoneally with infectious dose 2 × 106.5 TCID50 per mouse with CVB2/O or its mutants (CVB2/O/RD-II/VP1, CVB2/O/VP1-I118F, CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K and CVB2/O/2C-K185R) or mock-infected (control mice were given by 0.2 mL of phosphate buffer saline, PBS) as described previously (Vargová et al., 2003; Bopegamage et al., 2005). Mice were weighed regularly and sacrificed (three per group in time intervals) on days 0, 5, 7, 10, and 55 post-infections (p.i.). Blood, heart, and pancreas were collected for virological (snap frozen in liquid nitrogen) and histopathological (fixed in 4% formalin and paraffin embedded) investigation. Samples for virological examinations were stored at −80°C until analysis. Ethical Committee permission of the State Veterinary and Food Control Authority of the Slovak Republic, Č.k Ro 2522/13–221 (date 18 July 2013) was obtained and extended after 2 years. Extension number Ro 3248/16–221.
Presence of infectious virus
Snap-frozen organs (heart and pancreas) were thawed and frozen twice. Organ suspensions in PBS (10%) were prepared aseptically, antibiotics (200 U/mL penicillin and 0.2 mg/mL streptomycin) were added after sonification and centrifugation (Bopegamage et al., 2003; Bopegamage et al., 2005). Ten-fold diluted suspensions were added (four wells per dilution) to 24-h monolayers of HEp-2, GMK, and RD cells respectively, grown on 96-well flat-bottom in microtiter plates and incubated at 37°C with 5% CO2. Results were evaluated on days 5–7 p.i. To confirm the presence or absence of replicating virus (infectious virus in the organs) 2 blind passages were performed in GMK, HEp-2, and RD cells and observed for the presence of a cytopathic effect. The organs of the control mice were passaged only once.
Detection of viral RNA
Total RNA was extracted from snap-frozen organs of experimentally infected mice using the PureLink® RNA Mini Kit according to the manufacturer (Invitrogen, USA). The in-house two-step molecular method (PCR with reverse transcriptase and nested PCR) according to de Leeuw et al. (1994) and later modified in our laboratory (Bopegamage et al., 2005; Borsanyiova et al., 2024) was used to detect the EV genome. The primers were directed to the highly conserved sequences in the 5′untranslated region of the EV genome (Microsynth, Germany). Both, cDNA synthesis and amplifications were carried out in a single tube using the SuperScript III One-Step RT-PCR System with Platinum Taq High Fidelity (Invitrogen) and in the nested reaction, Platinum® PCR SuperMix High Fidelity (Invitrogen) was utilized. The PCR products were separated on a 2% agarose gel and visualized in Gel Documentation XR+ Imaging System (Bio-Rad).
Histopathological analysis
Sections (4–7 μm) of the formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded organs (pancreas and heart) were prepared and stained by hematoxylin and eosin methods. The histopathological changes were graded (1–4) for infiltration and necrosis as described previously (Bopegamage et al., 2003; Bopegamage et al., 2005; Cifuente et al., 2011).
Cytokine detection
In the pooled (3 mice/interval/group) sera of control and infected mice collected on days 5 and 7 p.i., cytokines Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), interferon (IFN)-γ, interleukin (IL)-1α, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-9, IL-10, IL-12, IL-13, IL-17, Keratinocyte-derived cytokine (KC), Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), Macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), RANTES (Regulated upon Activation, Normal T cell Expressed, and Secreted), Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) were determined using Quantibody® Mouse Cytokine Array 1 kit (RayBiotech, GA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Results
All mice used in the experimental infection survived until the end of the experiment, no mortality was observed.
Presence of infectious virus
Replicating virus was absent in the pancreas and heart of control mice. On day 5 p.i. CPE was observed only in the pancreas (1/3) of infected CD1 mice with CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K. In the hearts of infected CD1 mice, replicating virus was not detectable. Replicating virus in the organs was detected only in infected A/J mice at day 5 p.i. which was related to the mutants. Hearts of infected A/J mice with CVB2/O/RD-II/VP1 (1/3), CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K (2/3), and CVB2/O/2C-K185R (2/3), pancreas of CVB2/O (1/3), CVB2/O/VP1- I 118F (1/3) and CVB2/O/2C-K185R-infected mice (2/3) on day 5 p.i. showed cytopathic effects. No replicating virus was detected in organ suspensions of infected A/J or CD1 mice at days 7, 10, and 55 p.i.
Detection of viral RNA
Viral RNA was found in the hearts of all infected A/J mice on days 5 and 7 p.i except for two viruses (CVB2/O/RD-II/VP1 and CVB2/O) on day 7 p.i. (Table 1). At day 10 p.i., the heart (1/3) of CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K-infected A/J mice was positive, and the prolonged presence of viral RNA was detected only in the heart (1/3) of CVB2/O-infected A/J mice at day 55 p.i. During the acute phase of infection, viral RNA was noticed in the pancreas of all infected A/J mice until day 10 p.i. Prolonged presence of the virus was seen in the pancreas of CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K-infected A/J mice on day 55 p.i. RNA was absent in the heart and pancreas of CD1-infected mice, only the pancreas of CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K-infected mice revealed positivity on day 5 p.i. (2/3).
TABLE 1
| Organ | Heart | Pancreas | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day p.i. | 5 | 7 | 10 | 55 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 55 |
| CVB2/O | 1/3a | 0/3 | 0/3 | 1/3 | 3/3 | 2/3 | 2/3 | 0/3 |
| CVB2/O/RD-II/VP1 | 2/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 1/3 | 0/3 |
| CVB2/O/VP1-I118F | 2/3 | 2/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 1/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 0/3 |
| CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K | 2/3 | 3/3 | 1/3 | 0/3 | 3/3 | 2/3 | 2/3 | 1/3 |
| CVB2/O/2C-K185R | 1/3 | 1/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 0/3 |
The presence of viral RNA in the hearts and pancreases of A/J mice infected with CVB2/O and different mutants.
Number of positive mouse organs out of the total number of mice in the group (3).
Histopathological examination
Histopathological changes were absent in the hearts of both A/J and CD1 mice strains infected with the CVB2/O and mutants.
In infected CD1 mice, depending on the virus strain, a mild to moderate lymphocyte infiltration was observed in the pancreatic adipose tissue (except for CVB2/O, where no pancreatic changes were detectable); with CVB2/O/RD-II/VP1 on day 5 p.i., with CVB2/O/VP1-I118F on day 5 and 10 p.i. and in the case of CVB2/O/2C-K185R from day 7 until day 55 p.i. (Table 2). The mild to moderate interstitial lymphocytes infiltration in the exocrine pancreas was observed only in CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K-infected CD1 mice on day 5 p.i.
TABLE 2
| Mice type | A/J mice | CD1 mice | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Days post infection | D5 | D7 | D10 | D55 | D5 | D7 | D10 | D55 |
| CVB2/O | 0–1+ | 0 | 0 | 1+ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CVB2/O/RD-II/VP1 | 2+ | 0 | 1 + | 0 | 0–1+a | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CVB2/O/VP1-I118F | 0 | 1+ | 0 | 0 | 0–1a | 0 | 0–1+a | 0 |
| CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K | 2+ | 0–1+ | 0–1+ | 2 + | 0–1(±)b | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CVB2/O/2C-K185R | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0–1+a | 0–1+a | 0–1+a |
The histopathological score of pancreatic damage of A/J and CD-infected mice at different time intervals after infection with CVB2O and its mutants.
In adipose tissue.
Mild to moderate interstitial lymphocytes infiltration.
Pancreatitis was graded on a scale of 0 to 4 using a whole longitudinal section of the organ: a score of 0 corresponded to the absence of cellular infiltration or necrosis, 1 to minimal inflammation (1 to 5 foci), 2 to mild inflammation (less than 25% of the pancreas section affected), 3 to moderate inflammation (25 to 50% of the pancreas section affected) and 4 to severe inflammation (more than 50% of the pancreas tissue section showed infiltration or necrosis) (Bopegamage et al., 2003; Bopegamage et al., 2005; Cifuente et al., 2011).
Maximum pathological changes were identified in the pancreas of infected A/J mice. A mild interstitial mixed inflammatory infiltrate was observed in the pancreas of CVB2/O-infected A/J mice on day 5 p.i. and perivascular infiltrate in peripancreatic tissue on day 55 p.i. Infected A/J mice with CVB2/O/RD-II/VP1 and CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K showed similar changes in the pancreas on days 5 and 10 p.i. (minimal to mild mixed interstitial infiltrate), while in the CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K-infected A/J mice, focal interstitial lymphocyte inflammation of the exocrine pancreas persisted even on day 55 p.i. CVB2/O/VP1-I118F induced mild to moderate interstitial infiltration of the pancreas on day 7 p.i. and CVB2/O/2C-K185R did not produce any detectable changes in the pancreas. All observed histopathological changes were related to the exocrine pancreas. The histopathological changes in pancreatic tissue of CVB2/O and its mutants infected A/J mice are shown in Figure 1.
FIGURE 1
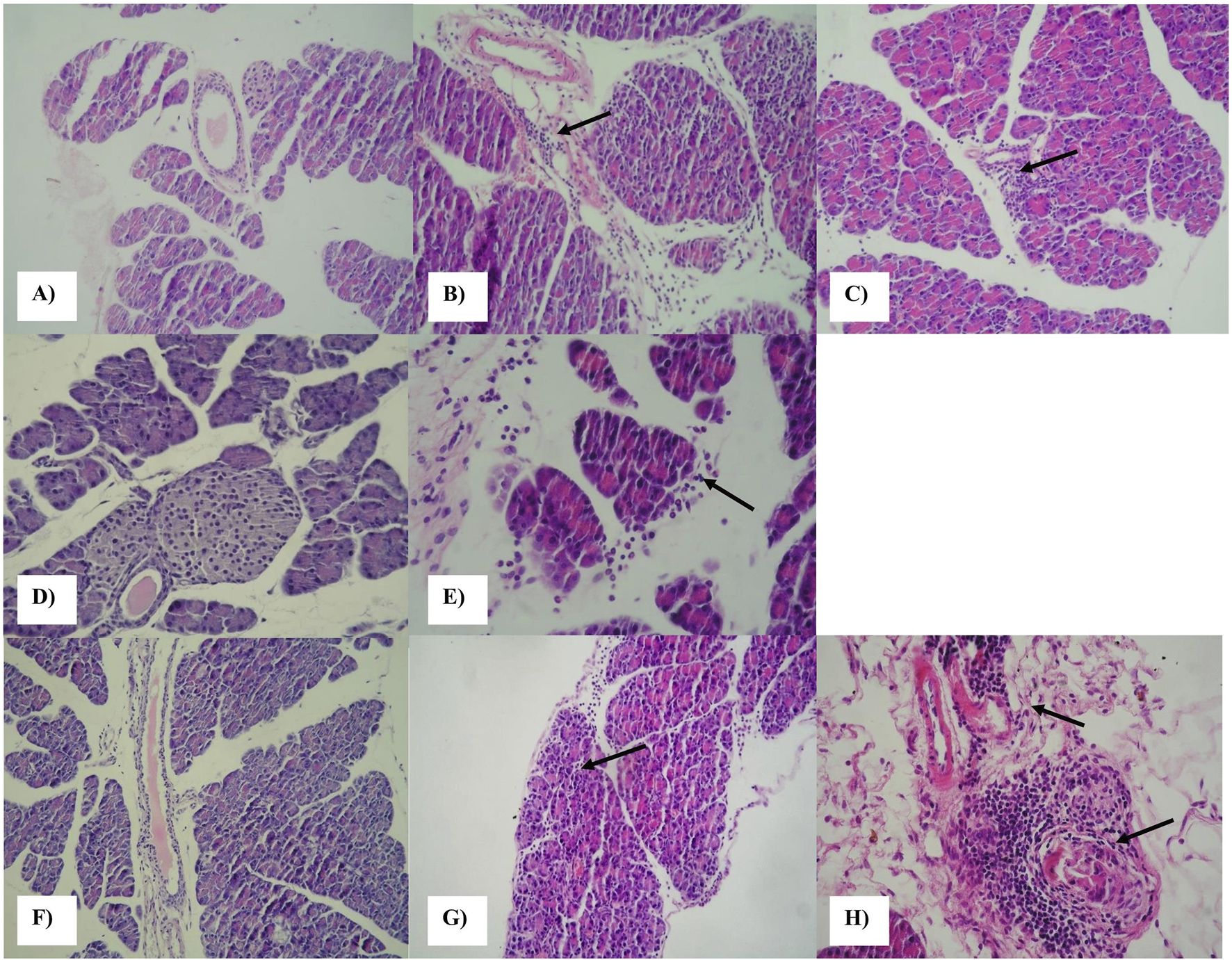
Histopathological changes in the pancreatic tissues of control and infected (CVB2/O and its mutants) A/J mice. Hematoxylin and eosin staining: (A) pancreas of control mice at day 5 p.i. (20x); (B) pancreas of CVB2/O-infected mice with mild inflammatory infiltrate at day 5 p.i. (20x); (C) CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K-infected A/J mice showing mild to moderate interstitial and perivascular infiltration of the exocrine pancreas at the day 5 p.i. (40x); (D) pancreas of control mice at day 10 p.i. (40x); (E) pancreas of CVB2/O/RD-II/VP1-infected A/J mice showing mild interstitial infiltration at the day 10 p.i. (40x); (F) pancreas of control mice at day 55 p.i. (20x); (G) pancreas of CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K-infected A/J mice showing interstitial inflammation of the pancreas at the day 55 p.i. (20x); (H) perivascular infiltrate in peripancreatic tissue of CVB2/O-infected mice at day 55 p.i. (40x).
Cytokine detection
The concentration of cytokines (pg/mL) in the pool sera of CVB2/O- and its mutants-infected A/J and CD1 mice were monitored on days 5 and 7 p.i. Variation in the cytokine production levels was observed, depending on the mouse strain and mutants (Table 3) and Supplementary graphs and Tables (Supplementary Tables S1A, S1B; Supplementary Graphs S1–S14).
TABLE 3
| B) cytokine (pg/ml) | Control | O* | ORD** | 118*** | 164**** | 185***** | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Days p.i. | 0 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 7 |
| GM-CSF | 4.9 | 10.4 | 10.8 | 7 | 13.6 | 8.8 | 14 | 6.8 | 22.6 | 3.6 | 13.4 | 10.6 | 2.2 |
| IFN-γ | 59.5 | 40.6 | 22.2 | 3.8 | 14.8 | 40.6 | 83.2 | 15.6 | 14.6 | 6.8 | 0 | 3.4 | 7.8 |
| IL-1a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 27.2 | 10.4 | 59 | 7 | 13.6 | 0 | 0.2 | 25.4 | 13.8 |
| IL-1b | 239.8 | 213.2 | 189.6 | 328.8 | 140.8 | 81 | 143 | 138.2 | 356.4 | 58.8 | 57 | 65.8 | 0 |
| IL-2 | 14.3 | 15.6 | 63.4 | 36.2 | 53.8 | 38.2 | 48.4 | 40 | 81.8 | 7.6 | 34.6 | 24 | 1 |
| IL-3 | 12.7 | 5.8 | 5.6 | 0 | 1.4 | 4 | 4.4 | 2 | 8 | 0 | 3.4 | 1.4 | 0 |
| IL-4 | 1.2 | 0.4 | 4.2 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 1.8 | 3.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0 | 0.8 |
| IL-5 | 40.8 | 24.6 | 23.8 | 8.8 | 12.2 | 17.8 | 13.2 | 21 | 19.2 | 5.2 | 5.4 | 6.8 | 12 |
| IL-6 | 94.2 | 60.8 | 60.6 | 26.4 | 40.8 | 73.8 | 147.4 | 21.6 | 46.8 | 20.2 | 1.8 | 47.8 | 42.2 |
| IL-9 | 228.9 | 330.6 | 893.2 | 107.6 | 321.8 | 294.6 | 417 | 353.4 | 395.4 | 76.2 | 406.6 | 157.6 | 406.6 |
| IL-10 | 36.3 | 79.2 | 110.2 | 46.2 | 117.8 | 63 | 109.6 | 49.6 | 192 | 12.4 | 91.2 | 61 | 73.4 |
| IL-12 | 18.5 | 4.8 | 15.2 | 3 | 0 | 2.4 | 10 | 3.6 | 26.2 | 0 | 0 | 0.6 | 0 |
| IL-13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 89 | 0 | 0 | 129.2 | 0 | 21.6 | 0 | 97 | 0 | 0 |
| IL-17 | 8.4 | 6.2 | 8 | 1.6 | 2.6 | 7.2 | 8.6 | 5.8 | 7.8 | 2.4 | 2.2 | 3.8 | 2.2 |
| KC | 4.8 | 20 | 9.4 | 3.4 | 0.2 | 13.8 | 15.2 | 6.8 | 5.2 | 1.8 | 3 | 15 | 4.4 |
| MCP-1 | 148.1 | 80.6 | 70.4 | 55.6 | 97.2 | 22.4 | 102.6 | 95.8 | 153.6 | 25.4 | 63.8 | 54.8 | 48.2 |
| M-CSF | 77.9 | 0 | 56.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 363 | 123.2 | 173 | 0 | 125.4 | 0 | 0 |
| RANTES | 18.9 | 28.4 | 14.4 | 10.4 | 4.4 | 17 | 12.6 | 11.4 | 2.4 | 4 | 4.2 | 7.4 | 8.6 |
| TNF-α | 118.2 | 288.8 | 368.6 | 120.4 | 202.8 | 151.4 | 311.4 | 303.8 | 265.2 | 0 | 141.8 | 318.6 | 120.6 |
| VEGF | 129.4 | 97.6 | 149.2 | 55.8 | 106 | 96.6 | 96.8 | 78.4 | 86.6 | 88.4 | 66.8 | 79.4 | 73.6 |
| B) Cytokine (pg/mL) | Control | O* | ORD** | 118*** | 164**** | 185***** | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Days p.i. | 0 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 7 |
| GM-CSF | 4.9 | 5 | 7 | 2 | 2.7 | 5 | 2.7 | 4.6 | 5.8 | 9.2 | 7.5 | 3 | 13.5 |
| IFN-γ | 59.5 | 16.6 | 9.4 | 2.9 | 0 | 2.7 | 0 | 0.8 | 8.1 | 7.7 | 7.8 | 1.6 | 14.5 |
| IL-1a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.4 | 0 | 30.9 | 4.3 | 14 | 0 | 2 | 19.8 | 34.6 |
| IL-1b | 239.8 | 130.5 | 93.1 | 0 | 0 | 11.7 | 0 | 19.7 | 93.1 | 134.4 | 76.6 | 36.8 | 114.4 |
| IL-2 | 14.3 | 30.2 | 23.7 | 9.9 | 0.8 | 6.9 | 0 | 7.8 | 23.5 | 20.9 | 15.2 | 0.2 | 20.8 |
| IL-3 | 12.7 | 3.8 | 3.5 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 4.4 | 5.3 | 2.9 | 0.4 | 6.8 |
| IL-4 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.2 | 0.9 | 1.3 | 0 | 2.2 |
| IL-5 | 40.8 | 12.3 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 2.4 | 0 | 0.3 | 9 | 7.5 | 8.6 | 6.8 | 10.1 |
| IL-6 | 94.2 | 15.5 | 26.7 | 8.6 | 37.1 | 43 | 20 | 6 | 25 | 17.1 | 24.3 | 39.8 | 34.7 |
| IL-9 | 228.9 | 302.1 | 259.7 | 82.1 | 242.1 | 233.7 | 191.1 | 45.1 | 356.8 | 341.9 | 306.1 | 129.6 | 573.8 |
| IL-10 | 36.3 | 76.8 | 78.3 | 28 | 17.9 | 27.1 | 38.3 | 0 | 78.2 | 84.9 | 52.6 | 17 | 118.5 |
| IL-12 | 18.5 | 11 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 2.8 | 0 | 0 | 6.7 | 4.3 | 0 | 0 | 19.9 |
| IL-13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 35.6 | 7.4 | 0 | 0 | 78.4 |
| IL-17 | 8.4 | 4.3 | 4 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 1.2 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 3.5 | 4 | 3.8 | 0.6 | 8.1 |
| KC | 4.8 | 2.4 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 0 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 3.1 | 2.1 | 1.9 | 0.3 | 0 | 3.2 |
| MCP-1 | 148.1 | 39.5 | 47.5 | 11.5 | 5.8 | 26.5 | 4.2 | 16.4 | 47.3 | 27.6 | 34.1 | 14.7 | 38.8 |
| M-CSF | 77.9 | 59 | 22.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 63.7 | 0 | 12.9 | 33.4 | 0 | 36.9 | 286.9 |
| RANTES | 18.9 | 10.4 | 17.4 | 22 | 9.8 | 8.5 | 11.3 | 13.8 | 9.8 | 14.4 | 9.9 | 18.5 | 13.5 |
| TNF-α | 118.2 | 93.6 | 80.3 | 0.8 | 0 | 29.6 | 0 | 15.9 | 108.7 | 75.4 | 168 | 57.1 | 183.1 |
| VEGF | 129.4 | 116.2 | 126.1 | 123.7 | 121.7 | 118.2 | 98.2 | 130 | 104.5 | 109.5 | 77.3 | 125.2 | 102.8 |
Cytokine concentration (pg/mL) in the pooled (3 mice/group) sera of CVB2/O- and its mutant’s-infected A/J (A) or CD1 mice (B) on days 5 and 7 p.i. (Based on Linear Regression Standard Curves).
*CVB2/O; **CVB2/O/RD-II/VP1; ***CVB2/O/VP1-I118F; ****CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K; *****CVB2/O/2C-K185R.
Higher levels of cytokines, CM-CSF, IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-10, IL-13, IL-17, MCP-1, M-CSF, and TNF-α, were present in infected A/J mice (depending on the virus used). The levels of IL-5, RANTES, and VEGF were lower than in the control serum for all the viruses used, while the cytokines IFN-γ, IL-3, IL-6, IL-9, IL-12, and KC showed a higher value only for the CVB2/O/RD-II/VP1 virus, respectively CVB2/O/VP1-I118F. The highest levels of various cytokines compared to control were observed when A/J mice were infected with CVB2/O/VP1-I118F, CVB2/O/RD-II/VP1, and CVB2/O.
In the infected A/J mice, we observed elevated cytokine levels between days 5 and 7 p.i. for each virus (wild type or mutant). Increased levels of the serum cytokines were found in CVB2/O/RD-II/VP1, CVB2/O/VP1-I118F, CVB2/O, and CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K. Mutant CVB2/O/2C-K185R showed a fall in the levels of 12 serum cytokines in A/J mice at day 7 p.i.
In infected CD1 mice cytokines (CM-CSF, IL-1α, IL-3, IL-6, IL-9, IL-10, IL-13, KC, M-CSF, RANTES, TNF-α, and VEGF) induction was higher as compared to the controls on days 5 or 7 p.i. depending on the virus used. Whereas IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-4, IL-5, IL-12, IL-17 were induced only in the case of CVB2/O/2C-K185R infection on day 7p.i. Totally in infected CD1 mice, mainly with CVB2/O/2C-K185R, but also with CVB2/O/VP1-I118F, and CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K elicited a greater cytokine response. Cytokines IL-2 and MCP-1 in the pool sera were lower than in controls. The viruses that induced the most reductions in levels of various cytokines were CVB2/O/RD-II/VP1, CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K, and CVB2/O, but reductions were also observed in several cytokines in mock-infected mice. The viruses that induced an increase in serum levels of up to 17 cytokines in CD1 mice between days 5 and 7, were CVB2/O/2C-K185R and CVB2/O/VP1-I118F. Increased levels of GM-CSF, a white blood cell growth factor, were found in all infected A/J mice except for CVB2/O/2C-K185R and in the sera of infected CD1 mice with CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K and CVB2/O/2C-K185R. Several increased values of proinflammatory (IFN-γ, IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-6, IL-9, IL-12, IL-17, KC, RANTES, TNF-α, VEGF) and anti-inflammatory (IL-4, IL-10, IL-13) cytokines were recorded depending on the virus type and mouse species. Overall, we can summarize that the highest levels of pro-inflammatory cytokine production in A/J mice were induced by CVB2/O/VP1-I118F, CVB2/O/RD-II/VP1, and CVB2/O, while IL-5, RANTES, and VEGF cytokine levels were lower than in controls for all viruses. In contrast, in infected CD1 mice, the CVB2/O/2C-K185R induced diverse cytokine production, followed by CVB2/O/VP1-I118F and CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K, and decreased cytokine levels in all infected CD1 mice were found for IL-2 and MCP-1 compared to the control group.
Discussion
In the process of attachment and entry into the cell, CVBs use coxsackie and adenovirus receptor (CAR) and decay accelerating factor (DAF) (Bergelson et al., 1995; Shafren et al., 1995; Bergelson et al., 1997; Martino et al., 1998; Martino et al., 2000; Dorner et al., 2005; Park et al., 2009; Cifuente et al., 2011). RD cells are known to express DAF without clear CAR expression. A persistent infection in RD cells, adapted to a cytolytic replication in these cells (CVB2/O/RD) by generating 3 single laboratory induced mutations in the original CVB2/O prototype which was related to the cytolytic activity was shown by Gullberg et al. (2010). It was found that CVB2/O/RD-induced cytolysis was associated with an apoptotic response. Moreover, although the nonstructural 2C enteroviral protein is multifunctional, a single substitution (K185R) was not an essential element for the cytolytic infection. Single mutation of the viral protein VP1 at position Q164K played a pivotal role in the establishment of cytolytic replication and induction of an apoptotic response in RD cells. CVBs are known to induce pancreatitis in experimental mice models (Tracy et al., 2000; Huber and Ramsingh, 2004). Important factors in determining the outcome of CVB-induced mouse disease include age, inoculation method, mouse strain, nutritional status, and virus genotype. The VP1 and, to a lesser extent, the VP4 region in CVB4 are thought to be major pathogenic determinants of pancreatic disease, but multiple nucleotides in the genome have been identified as pathogenic determinants. The overall pathogenic phenotype also depends on the specific CVB variant (Chapman et al., 1997; Pallansch et al., 2013; Cifuente et al., 2011). In the present work, we followed infections with CVB2/O and its laboratory mutants over a prolonged period, and their impact on pathogenesis in the mice (in vivo system as compared to the previously studied in vitro systems). Our results showed that the changes were not prominent in the hearts so we focused on murine pancreatitis. Our rationale was to compare the pathogenesis of CVB2 and its mutants in two types of mouse models. A/J inbred mice which are known to be sensitive (defective in macrophage function, develop moderate to severe inflammation following CVB3 infection) to CVB infections showing histopathological changes in organs, and less sensitive CD1 outbred mice. Our previous experience shows (Precechtelova et al., 2015) that this outbred strain is less susceptible as compared to Swiss albino outbred mice. Furthermore, we were interested in comparing the viral pathogenesis of different mutants (CVB2/O/RD-II/VP1, CVB2/O/VP1-I118F, CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K, CVB2/O/2C-K185R) and CVB2/O. An identical infectious dose for all viruses used was important to ensure standard conditions and evaluation of the experiment. All viruses induced CPE (microscopically visible) on GMK cells, CVB2/O/RD-II/VP1 and CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K mutants also on RD cells, and Hep-2 cells. To detect the presence of replicating viruses, we passaged the organs in these susceptible cell lines. Induced histopathological changes and the presence of viral RNA were the two main characteristics compared in mice. The pro-inflammatory [Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), interferon (IFN)-γ, interleukin (IL)-1α, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-3, IL-6, IL-9, IL-12, IL-17, Keratinocyte-derived cytokine (KC), Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), Macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), RANTES (Regulated upon Activation, Normal T cell Expressed, and Secreted), Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)]and anti-inflammatory cytokines [IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, IL-13] were analyzed to observe the association between the histopathological changes, viral RNA, and presence of replicating virus. Infectious virus was demonstrated in organs in which enteroviral RNA, was confirmed. The presence of viral RNA was demonstrated in the pancreases of infected mice that showed infiltration of exocrine tissue (in both A/J and CD1 mice). We did not demonstrate the presence of virus in the pancreas of CD1 mice that showed histopathological changes in pancreatic adipose tissue. Histopathological changes in the pancreatic adipose tissue of CVB2/O/2C-K185R-infected CD1 mice persisted until the end of the experiment and were accompanied (in the acute phase of infection) with highest cytokine levels. In contrast, pancreatic infection in CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K-infected A/J mice lasted until the end of the study, manifested by damage to the exocrine pancreas, was accompanied by the least induction of cytokines in the acute phase of infection. We did not observe mortality or morbidity in infected mice.
Histopathological changes were absent in the hearts of both infected CD1 and A/J mice. In infected CD1 mice, infiltration was demonstrated mainly in the pancreatic adipose tissue, or in the exocrine pancreas (CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K-infected mice). Histopathological changes in the pancreas were noted especially in CVB2/O/RD-II/VP1- and CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K-infected A/J mice. CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K-infected A/J mice showed focal interstitial lymphocyte infiltration in the exocrine pancreas on day 55 p.i. The destructive impact of CVB2/O/2C-K185R on the exocrine pancreas was not proven, although within 10 days p.i. was evidenced the viral RNA in the tissue of A/J mice. Our results are consistent with previous results of the pilot study (Gullberg et al., 2010), in which the pathogenesis of two viruses (CVB2/O and triple mutant CVB2/O/RD) was investigated, and only the acute phase of infection (day 5 p.i.) was monitored. At the time of development of paralytic symptoms, Roberts and Boyd (1987) observed pancreatitis without affecting the islets of Langerhans in one-third of newborn mice inoculated both intracerebrally and subcutaneously with CVB2. Other authors (Hong et al., 2017) studied the effect of infection of patients’ isolates (CB2/04/243, CB2/04/279) and the prototype strain CVB2/O on pathogenesis in BALB/c mice. On days 7 and 13 p.i., mice developed extensive inflammation in the exocrine pancreas but not in islets, however, the B2/04/243-infected mice showed mild inflammation. Inflammation of acinar cells was noted, but the islets of Langerhans were intact. The differences in pancreatic histopathological changes in A/J mice may be related not only to diverse cytokines response, but also to the long-term presence of the virus in the pancreatic tissue.
Vreugdenhil et al. (2000) studied the cytokine response of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells to EVs (CVB4 and poliovirus) infection. It resulted in the production of IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-2, IFN-γ, and IL-10, but not significant levels of IL-4. Other authors observed the serum levels of cytokines (IL-6, IL-10, and IL-13) in EV-A71-infected patients with Hand, foot, and mouth disease and found significantly higher levels of these circulating cytokines compared to healthy individuals (Chen et al., 2014). During CVB infection, in addition to neutralizing antibodies, non-neutralizing antibodies can be formed, which can facilitate or enhance CVB4 infection in vitro, with subsequent increased production of IFN-α and inflammatory cytokines (Chehadeh et al., 2001; Hober et al., 2002; Chehadeh et al., 2005; Alidjinou et al., 2013). Increased levels of the proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, as well as IFN-α were detected in cultured human pancreatic islet endothelial cells after CVB4 infection in vitro (Zanone et al., 2007). Another research team (Schulte et al., 2012) investigated the induction of human pancreatic islet culture cytokines following infection with CVB3, CVB4 (E2 and Tilo), and EV1 (Farouk) 48 h p.i. They noted that high levels of IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1 may be due in part to stress, and VEGF may be induced by damaged islet epithelium. After CVB3 infection, IL-6, RANTES, IL-8, macrophage inflammatory protein, and GM-CSF were significantly increased, whereas IL-1β, IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, and MCP-3 levels remained at undetectable or very low levels. CVB4 E2 and EV1 strains showed cytokine expression similar to CVB3 with induction but with some delay of IL-6 and IL-8, whereas the response to CVB4 Tilo was somewhat less pronounced (fewer virus-positive cells in the islets). Using UV-inactivated CVB3, was shown that virus replication is required for the induction of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines. The cytokine balance is critical in determining the histopathological and immunological responses in a murine model during CVB infection. The cytokine response may lead to a strong systemic immune induction triggered by a network of immunological signaling pathways resulting in a variety of histopathological changes (Park et al., 2009).
Cytokines act as specific intercellular messengers that regulate immune response, particularly by modulating the balance between humoral and cell-mediated responses, and thereby contribute to the regulation of inflammation, homeostasis, apoptosis, differentiation, and proliferation (Coondoo, 2011; Coico and Sunshine, 2015; Heuertz and Ezekiel, 2016). Some cytokines act to exacerbate disease (proinflammatory), whereas others serve to reduce inflammation and promote healing (anti-inflammatory). Proinflammatory cytokines induced by activated innate immune cells have an essential role in clearing enteric pathogens (Dinarello, 2000). We have studied the pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines during the acute phase of infection (on days 5 and 7 p.i.). Our aim was to observe the presence of individual cytokines, or their combination, could also contribute to pancreatic tissue damage. Pooling of sera of the mice at each interval and no monitoring of the local presence of cytokines in the pancreas tissue are two major limiting factors in the interpretation of our cytokine studies. However, our studies show that production of anti-inflammatory cytokines differed in A/J and CD1 mice depending on the infected virus strain. Pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1α, IL-6, RANTES, VEGF, IL-1α, TNF-α, GM-CSF, IL-3, IL-6, IL-9, KC, and others were detected on histopathological findings in CD1 mice infection, with the highest diversity demonstrated in the CVB2/O/2C-K185R mutant. In A/J mice, various inflammatory cytokines such as IL-2, IL-6, GM-CSF, IL-1α, MCP-1, M-CSF, TNF-α, and others were induced in A/J mice, with the highest production induced by the CVB2/O/VP1-I118F mutant. Interestingly, the CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K mutant, which induced more severe damage to the pancreas of A/J mice and long-term persistence of the virus in the tissue, induced the production of only GM-CSF, M-CSF cytokines. We could not correlate the cytokine levels and viral pathogenesis.
In conclusion the mouse strains and virus mutations played an important role in the pathogenesis of CVB2 infection. A/J mice were more susceptible to CVB2 infection as compared to the CD1 mice.
The CVB2/O strain, affects mainly the heart and central nervous system, which is in agreement with (Hong et al., 2017; Hopkins et al., 2019; Ushoida et al., 2020). The mutants did not cause serious damage of the mice heart, but we detected damage to the pancreas. CD1 mice were less susceptible to CVB2 infection. CVB2/O/VP1-I118F and CVB2/O/2C-K185R mutants were least destructive in mouse pancreas, although the presence of various cytokines in the acute phase of infection was high compared to CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K. The CVB2/O/VP1-Q164K mutant induced marked changes in the exocrine pancreas of infected A/J mice till the end of the experiment. We therefore suggest that the single changed amino acid in the VP1 protein of CVB2/O was identified as a potential virulence factor in the pancreas and caused prolonged presence of viral RNA and low viral clearance. This study has provided partial insights into understanding the pathogenesis of the prototype CVB2/O strain and its laboratory genetic variation, focusing on strategic vaccination options, but further detailed studies are needed.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by State Veterinary and Food Administration of the Slovak Republic number Č.k Ro 2522/13-221 (date 18 July 2013). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
All authors contributed to the article and approved it for publication. Conceptualization: AL and SB; methodology: MB, KB, BB; writing-original draft preparation: MB; writing-review and editing: BB, MP, and SB. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Reference Center for Identification of Enteric viruses, Slovak Medical University in Bratislava, and the Norwegian financial support mechanism, Mechanism EEA and Slovak Government [SK0082].
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Maria Gullberg for her intense involvement and valuable advice given during this study when she worked at the Linnaeus University in Kalmar, Sweden with prof. AL.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontierspartnerships.org/articles/10.3389/av.2025.12740/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
A/J, inbred A/JOlaHsd mice; CAR, coxsackie and adenovirus receptor; CD1, mice derived from a group of outbred Swiss albino mice; CVs, coxsackieviruses; DAF, decay accelerating factor; EMEM, Eagle´s minimum essential medium; EV, enteroviruses; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; GMK, green monkey kidney cells; HEp-2, human laryngeal cancer cells; HEPES, 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; KC, keratinocyte-derived cytokine; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; M-CSF, macrophage colony-stimulating factor; p.i., post infection; PBS, phosphate buffer saline; RANTES, regulated upon Activation, Normal T cell Expressed, and Secreted; RD, human rhabdomyosarcoma cells; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VP, viral capsid protein.
References
1
Alidjinou E. K. Sané F. Engelmann I. Hober D. (2013). Serum-dependent enhancement of coxsackievirus B4-induced production of IFNα, IL-6 and TNFα by peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J. Mol. Biol.425, 5020–5031. 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.10.008
2
Argo E. Gimenez B. Cash P. (1992). Non-cytopathic infection of rhabdomyosarcoma cells by coxsackie B5 virus. Arch. Virol.126, 215–229. 10.1007/BF01309696
3
Bergelson J. M. Cunningham J. A. Droguett G. Kurt-Jones E. A. Krithivas A. Hong J. et al (1997). Isolation of a common receptor for Coxsackie B viruses and adenoviruses 2 and 5. Science275, 1320–1323. 10.1126/science.275.5304.1320
4
Bergelson J. M. Mohanty J. G. Crowell R. L. St John N. F. Lublin D. M. Finberg R. W. (1995). Coxsackievirus B3 adapted to growth in RD cells binds to decay-accelerating factor (CD55). J. Virol.69, 1903–1906. 10.1128/JVI.69.3.1903-1906.1995
5
Bopegamage S. Borsanyiová M. Vargová A. Petrovicová A. Benkovicová M. Gomolcák P. (2003). Coxsackievirus infection of mice. I. Viral kinetics and histopathological changes in mice experimentally infected with coxsackieviruses B3 and B4 by oral route. Acta Virol.47, 245–251.
6
Bopegamage S. Kovacova J. Vargova A. Motusova J. Petrovicova A. Benkovicova M. et al (2005). Coxsackie B virus infection of mice: Inoculation by the oral route protects the pancreas from damage, but not from infection. J. Gen. Virol.86, 3271–3280. 10.1099/vir.0.81249-0
7
Borsanyiova M. Bopegamage S. Vari S. G. (2024). Efficacy of sample collection without virus transport medium in suspected enteroviral infections for molecular diagnosis. Bratisl. Med. J.125, 219–222. 10.4149/bll_2024_33
8
Chapman N. M. Ramsingh A. I. Tracy S. (1997). Genetics of coxsackievirus virulence. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 223. 227–258. 10.1007/978-3-642-60687-8_11
9
Chehadeh W. Bouzidi A. Alm G. Wattré P. Hober D. (2001). Human antibodies isolated from plasma by affinity chromatography increase the coxsackievirus B4-induced synthesis of interferon-alpha by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro. J. Gen. Virol.82, 1899–1907. 10.1099/0022-1317-82-8-1899
10
Chehadeh W. Lobert P. E. Sauter P. Goffard A. Lucas B. Weill J. et al (2005). Viral protein VP4 is a target of human antibodies enhancing coxsackievirus B4- and B3-induced synthesis of alpha interferon. J. Virol.79, 13882–13891. 10.1128/JVI.79.22.13882-13891.2005
11
Chen Z. Li R. Xie Z. Huang G. Yuan Q. Zeng J. (2014). IL-6, IL-10 and IL-13 are associated with pathogenesis in children with Enterovirus 71 infection. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med.7, 2718–2723.
12
Cifuente J. O. Ferrer M. F. Jaquenod de Giusti C. Song W. C. Romanowski V. Hafenstein S. L. et al (2011). Molecular determinants of disease in coxsackievirus B1 murine infection. J. Med. Virol.83, 1571–1581. 10.1002/jmv.22133
13
Coico R. Sunshine G. (2015). “Cytokines,” in Immunology: a short course. 7th ed. (Hoboken, USA: JohnWiley and Sons), 176–193.
14
Coondoo A. (2011). Cytokines in dermatology - a basic overview. Indian J. ddermatol.56, 368–374. 10.4103/0019-5154.84717
15
de Leeuw N. Melchers W. J. G. Willemse D. F. M. Balk A. H. M. M. de Jonge N. Galama J. M. D. (1994). The diagnostic value of PCR for the detection of enteroviral infections. Serodiagn. Immunother. Infect. Dis.6, 189–195. 10.1016/0888-0786(94)90031-0
16
Dinarello C. A. (2000). Proinflammatory cytokines. Chest118, 503–508. 10.1378/chest.118.2.503
17
Domingo E. Martin V. Perales C. Escarmis C. (2008). Coxsackieviruses and quasispecies theory: Evolution of enteroviruses. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol.323, 3–32. 10.1007/978-3-540-75546-3_1
18
Dorner A. A. Wegmann F. Butz S. Wolburg-Buchholz K. Wolburg H. Mack A. et al (2005). Coxsackievirus-adenovirus receptor (CAR) is essential for early embryonic cardiac development. J.Cell Sci.118, 3509–3521. 10.1242/jcs.02476
19
Fratty I. S. Kriger O. Weiss L. Vasserman R. Gabai R. Erster O. et al (2024). Molecular analysis of coxsackievirus B2 associated with severe symptoms of the central nervous system. J. Med. Virol.96, e70066. 10.1002/jmv.70066
20
Frisk G. Lindberg M. A. Diderholm H. Oiderholm H. (1999). Persistence of coxsackievirus B4 infection in rhabdomyosarcoma cells for 30 months. Brief report. Brief. Rep. Arch. Virol.144, 2239–2245. 10.1007/s007050050638
21
Gullberg M. Tolf C. Jonsson N. Polacek C. Precechtelova J. Badurova M. et al (2010). A single coxsackievirus B2 capsid residue controls cytolysis and apoptosis in rhabdomyosarcoma cells. J. Virol.84, 5868–5879. 10.1128/JVI.02383-09
22
Heuertz R. M. Ezekiel U. R. (2016). “Cytokines,” in Clinical immunology and serology: a laboratory perspective. Editors StevensC. H. D.MillerL. E. (Philadelphia F.A. Davis Company), 77–90.
23
Hierholzer J. C. Killington R. A. (1996). Virus isolation and quantitation. Virol. Methods Man., 25–46. 10.1016/B978-012465330-6/50003-8
24
Hober D. Chehadeh W. Weill J. Hober C. Vantyghem M. C. Gronnier P. et al (2002). Circulating and cell-bound antibodies increase coxsackievirus B4-induced production of IFN-alpha by peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with type 1 diabetes. J. Gen. Virol.83, 2169–2176. 10.1099/0022-1317-83-9-2169
25
Hong J. Kang B. Yeo S. Jee Y. Park J. H. (2017). Pathogenesis of coxsackievirus B2 in mice: Characterization of clinical isolates of the coxsackievirus B2 from patients with myocarditis and aseptic meningitis in korea. J. Vet. Sci.18, 457–464. 10.4142/jvs.2017.18.4.457
26
Hopkins K. A. Abdou M. H. Hadi M. A. (2019). Coxsackie B2 virus infection causing multiorgan failure and cardiogenic shock in a 42-year-old man. Tex. Heart Inst. J.46, 32–35. 10.14503/THIJ-17-6361
27
Huang H. W. Chen Y. S. Chen J. Y. Lu P. L. Lin Y. C. Chen B. C. et al (2015). Phylodynamic reconstruction of the spatiotemporal transmission and demographic history of coxsackievirus B2. BMC Bioinforma.16, 302. 10.1186/s12859-015-0738-2
28
Huber S. Ramsingh A. I. (2004). Coxsackievirus-induced pancreatitis. Viral Immunol.17, 358–369. 10.1089/vim.2004.17.358
29
Kärber G. (1931). Beitrag zur kollektitoven behandlung pharmakologischer Reihenversuche. Arch. Exp. Pathol. Pharm.162, 480–483. 10.1007/BF01863914
30
Khetsuriani N. Lamonte-Fowlkes A. Oberst S. Pallansch M. A. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2006). Enterovirus surveillance--United States, 1970-2005. MMWR Surveill. Summ.55, 1–20.
31
Kriger O. Abramovich A. Fratty I. S. Leshem E. Amit S. Stein M. et al (2023). An outbreak of coxsackievirus B type 2 acute meningoencephalitis in children, Israel, july-september 2022. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J.42, e177–e179. 10.1097/INF.0000000000003876
32
Lukashev A. N. (2005). Role of recombination in evolution of enteroviruses. Rev. Med. Virol.15, 157–167. 10.1002/rmv.457
33
Machado R. S. Tavares F. N. Sousa I. P. Jr. (2024). Global landscape of coxsackieviruses in human health. Virus Res.344, 199367. 10.1016/j.virusres.2024.199367
34
Martino T. A. Petric M. Brown M. Aitken K. Gauntt C. J. Richardson C. D. et al (1998). Cardiovirulent coxsackieviruses and the decay-accelerating factor (CD55) receptor. Virology244, 302–314. 10.1006/viro.1998.9122
35
Martino T. A. Petric M. Weingartl H. Bergelson J. M. Opavsky M. A. Richardson C. D. et al (2000). The coxsackie-adenovirus receptor (CAR) is used by reference strains and clinical isolates representing all six serotypes of coxsackievirus group B and by swine vesicular disease virus. Virology271, 99–108. 10.1006/viro.2000.0324
36
Pallansch M. A. Oberste M. S. Whitton J. L. (2013). “Enteroviruses: polioviruses, coxsackieviruses, echoviruses and newer enteroviruses,” in Fields virology. Editors KnipeD. M.HowleyP. M.6th ed. (Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins), 490–530. Volume 1.
37
Park J. H. Kim D. S. Cho Y. J. Kim Y. J. Jeong S. Y. Lee S. M. et al (2009). Attenuation of coxsackievirus B3 by VP2 mutation and its application as a vaccine against virus-induced myocarditis and pancreatitis. Vaccine27, 1974–1983. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.01.008
38
Polacek C. Ekström J. O. Lundgren A. Lindberg A. M. (2005). Cytolytic replication of coxsackievirus B2 in CAR-deficient rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Virus Res.113, 107–115. 10.1016/j.virusres.2005.04.021
39
Polacek C. Lundgren A. Andersson A. Lindberg A. M. (1999). Genomic and phylogenetic characterization of coxsackievirus B2 prototype strain Ohio-1. Virus Res.59, 229–238. 10.1016/s0168-1702(98)00140-3
40
Precechtelova J. Borsanyiova M. Stipalova D. Sarmirova S. Gomolcak P. Berakova K. et al (2015). Pathophysiology of the pancreas after oral infection of genetically diverse mice with coxsackievirus B4-E2. Arch. Virol.160, 103–115. 10.1007/s00705-014-2236-7
41
Roberts G. B. Boyd J. F. (1987). The histopathology of enterovirus infections of new-born mice. J. Infect.15, 45–56. 10.1016/s0163-4453(87)91426-5
42
Schmidtke M. Selinka H. C. Heim A. Jahn B. Tonew M. Kandolf R. et al (2000). Attachment of coxsackievirus B3 variants to various cell lines: Mapping of phenotypic differences to capsid protein VP1. Virology275, 77–88. 10.1006/viro.2000.0485
43
Schulte B. M. Lanke K. H. Piganelli J. D. Kers-Rebel E. D. Bottino R. Trucco M. et al (2012). Cytokine and chemokine production by human pancreatic islets upon enterovirus infection. Diabetes61, 2030–2036. 10.2337/db11-1547
44
Shafren D. R. Bates R. C. Agrez M. V. Herd R. L. Burns G. F. Barry R. D. (1995). Coxsackieviruses B1, B3, and B5 use decay accelerating factor as a receptor for cell attachment. J. Virol.69, 3873–3877. 10.1128/JVI.69.6.3873-3877.1995
45
Sousa I. P. Jr Machado R. S. Burlandy F. M. Silva E. E. D. (2020). Detection and characterization of a coxsackievirus B2 strain associated with acute meningoencephalitis, Brazil, 2018. Rev. Soc. Bra. Med. Trop.54, e20190499. 10.1590/0037-8682-0499-2019
46
Spearman C. (1908). The method of ‘right and wrong cases’ (‘CONSTANT stimuli’) without GAUSS'S formulae. Brit. J. Psychol.2, 227–242. 10.1111/j.2044-8295.1908.tb00176.x
47
Tracy S. Höfling K. Pirruccello S. Lane P. H. Reyna S. M. Gauntt C. J. (2000). Group B coxsackievirus myocarditis and pancreatitis: Connection between viral virulence phenotypes in mice. J. Med. Virol.62, 70–81. 10.1002/1096-9071(200009)62:1<70::aid-jmv11>3.0.co;2-r
48
Ushioda W. Kotani O. Kawachi K. Iwata-Yoshikawa N. Suzuki T. Hasegawa H. et al (2020). Neuropathology in neonatal mice after experimental coxsackievirus B2 infection using a prototype strain, Ohio-1. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol.79, 209–225. 10.1093/jnen/nlz124
49
Vargová A. Bopegamage S. Borsanyiová M. Petrovicová A. Benkovicová M. (2003). Coxsackievirus infection of mice. II. Viral kinetics and histopathological changes in mice experimentally infected with coxsackievirus B3 by intraperitoneal route. Acta Virol.47, 253–257.
50
Vreugdenhil G. R. Wijnands P. G. Netea M. G. van der Meer J. W. Melchers W. J. Galama J. M. (2000). Enterovirus-induced production of pro-inflammatory and T-helper cytokines by human leukocytes. Cytokine12, 1793–1796. 10.1006/cyto.2000.0786
51
Zanone M. M. Favaro E. Ferioli E. Huang G. C. Klein N. J. Perin P. C. et al (2007). Human pancreatic islet endothelial cells express coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor and are activated by coxsackie B virus infection. FASEB J.21, 3308–3317. 10.1096/fj.06-7905com
52
Zhang J. Zhang H. Zhao Y. Guo C. Yang Z. Ma S. (2017). Molecular characterization of a new human coxsackievirus B2 associated with severe hand-foot-mouth disease in Yunnan Province of China in 2012. Arch. Virol.162, 307–311. 10.1007/s00705-016-3075-5
53
Zhang M. Xu D. Feng C. Guo W. Fei C. H. Sun H. et al (2022). Isolation and characterization of a novel clade of coxsackievirus B2 associated with hand, foot, and mouth disease in Southwest China. J. Med. Virol.94, 2598–2606. 10.1002/jmv.27657
Summary
Keywords
coxsackievirus B2, mouse model, intraperitoneal infection, pathogenesis, mutant
Citation
Borsanyiova M, Berakova K, Benkoova B, Pellerova M, Lindberg AM and Bopegamage S (2025) Intraperitoneal infection of A/J and CD1 mice with coxsackievirus B2 and its mutants. Acta Virol. 69:12740. doi: 10.3389/av.2025.12740
Received
25 January 2024
Accepted
04 July 2025
Published
22 July 2025
Volume
69 - 2025
Edited by
Katarina Polcicova, Slovak Academy of Sciences, Slovakia
Reviewed by
Karolína Tomčíková, University of Trnava, Slovakia
Ling Tao, Xinxiang Medical University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Borsanyiova, Berakova, Benkoova, Pellerova, Lindberg and Bopegamage.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Maria Borsanyiova, maria.borsanyiova@szu.sk
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.